
The leukemias and lymphomas represent a group of heterogeneous myeloid or lymphoid clonal stem cell disorders with variable clinical presentation, pathological characteristics, prognosis and recommendations for treatment.[1]

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


The leukemias and lymphomas represent a group of heterogeneous myeloid or lymphoid clonal stem cell disorders with variable clinical presentation, pathological characteristics, prognosis and recommendations for treatment.[1]
The management of leukemias and lymphomas now includes the use of many targeted therapies. Nurses need to have an understanding of the targeted therapies and their side effects so they can appropriately manage the side effects that their patients with leukemias and lymphomas may experience.
Two researchers from the Mayo Clinic have published an editorial calling for new approaches in the treatment of AML, arguing that "using the same old drugs in different doses or different schedules is not going to cut it."

Cancer treatment is undergoing significant developments and entering the new golden era of genomics which has true potentials for the promise of personalized medicine. Large-scale sequencing is changing our understanding of malignant disorders particularly acute myeloid leukemia.
Inotuzumab ozogamicin has achieved a markedly long antitumor response in patients with refractory or relapsed indolent B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) in an ongoing phase II study. Interim findings were reported by lead investigator Kenneth Luu, PhD, associate director of Pfizer global R&D.
A combination of TL32711, an investigational second mitochondrial-derived activator of caspases (Smac), and tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis inducing ligand at low concentrations produced marked apoptosis in germinal center lines, with minimal to no effect for each agent alone.
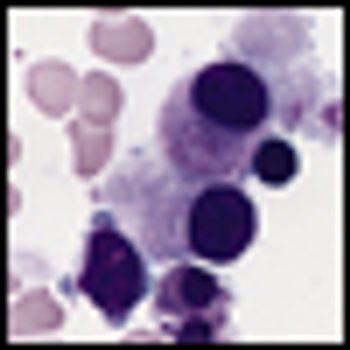
Preliminary findings of a phase I/II randomized clinical trial indicate that SGI-110, a novel DNA methylation inhibitor, is safe, well tolerated and efficacious in patients with acute myelogenous leukemia.

When light-chain amyloidosis is diagnosed prior to the development of advanced cardiomyopathy, systemic therapy is capable of producing hematologic responses that will translate into organ responses and prolonged survival. Advances in the management of multiple myeloma are currently being translated into a variety of clinical trials designed to improve the quality of life and survival of patients with light-chain amyloidosis.

In this article, we review the current knowledge on the biological findings, clinical features, and therapeutic approaches for splenic marginal zone lymphoma.

Four publications on cancer treatment during pregnancy were published last week in the journal Lancet, serving as new treatment guidelines for chemotherapy and surgery in pregnant patients with solid tumors and hematologic malignancies.

In the current issue of ONCOLOGY, Gertz and Dispenzieri provide a scholarly review of the early recognition, diagnosis, and treatment of immunoglobulin light-chain (AL) amyloidosis.

Immunoglobulin light chain (AL) amyloidosis develops in 2% of individuals with monoclonal plasma cell dyscrasias. In this issue of ONCOLOGY, Drs. Gertz and Dispenzieri discuss AL amyloidosis, highlighting progress in the field along with outstanding challenges.

Splenic lymphomas are a diverse group of lymphoid malignancies that have clinical behavior ranging from indolent to aggressive and that have both B-cell and T-cell histologies.

The article by Thieblemont and colleagues very nicely summarizes the key pathogenetic and diagnostic features and present treatment of splenic marginal zone lymphoma (SMZL).

The aim of this review is twofold: to summarize descriptions of the clinical presentation provided in published series in order to help clinicians recognize and treat patients, and to discuss diagnostic difficulties faced by hematopathologists when dealing with these lesions and others in the differential diagnosis that must be distinguished from one another.

The results of the 2-year follow-up of the dasatinib DASISION phase III trial show the continued superiority of the drug compared to imatinib. The results provide further support for treatment of first-line chronic phase chronic myeloid leukemia patients that harbor the Philadelphia chromosome.

The phase III randomized RESORT (ECOG Protocol E4402) trial asked whether a maintenance schedule of rituximab every 3 months would lead to a superior disease control outcome compared to retreatment upon progression. The answer, presented this week at ASH, is no.
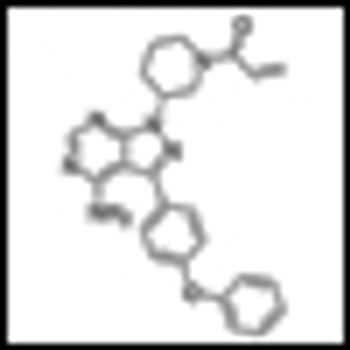
Updated findings from a multicenter phase Ib/II clinical trial suggest that the novel Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor PCI-32765 may be an important new targeted treatment approach for patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
Researchers presented a late-breaking abstract reporting activity in a metastatic lymphoma mouse model of two monoclonal antibodies combined with CpG, a short synthetic oligonucleotide agonist of TLR9, that mimic bacterial and viral DNA and facilitates a pro-inflammatory immune response.
The first plenary session at this year’s ASH was kicked off by the presentation of a study that showed that when stem cells come from donors unrelated to the patient there is no difference in patient survival between the use of cells sourced from peripheral blood or bone marrow.

The phase III trial comparing the use of gemtuzumab ozogamicin combined with chemotherapy to chemotherapy alone in newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia (AML) patients provides evidence that the combination treatment may be promising in this patient population.
Obinutuzumab (GA101) achieved higher response rates than rituximab in the first head-to-head trial of the two biologic agents in patients with relapsed non-Hodgkin lymphoma.

CancerNetwork highlights four sessions--on anaplastic large cell lymphoma, lymphoma in pregnancy, follicular lymphoma, splenic marginal zone lymphoma--you won’t want to miss from this year’s ASH.

The US Food and Drug Administration has approved asparaginase Erwinia chrysanthemi for the treatment of patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia, who have developed hypersensitivity to E. coli derived asparaginase and pegaspargase chemotherapy.

Two recent reports show that the prognosis of MDS patients after secondary failure of hypomethylating drugs is poor, and switching from one failing hypomethylating drug to another cannot induce clinically significant responses.