Researchers tested the addition of the T cell–boosting decitabine to anti–PD-1 therapy with camrelizumab among patients with relapsed or refractory classic Hodgkin lymphoma.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


Researchers tested the addition of the T cell–boosting decitabine to anti–PD-1 therapy with camrelizumab among patients with relapsed or refractory classic Hodgkin lymphoma.
The MYD88 driver mutation was detected in the cerebrospinal fluid of a majority of patients with CNS lymphoma, indicating its potential utility as a diagnostic and monitoring tool.

Researchers looked at the treatment failure rate for immunotherapy with R-CHOP in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma who were occupationally exposed to pesticides.

Researchers compared the newly developed PRIMA-PI risk score against FLIPI and FLIPI-2 in patients with follicular lymphoma.
A retrospective study supported the role of primary radiotherapy in early-stage follicular lymphoma.

Researchers tested the PI3K inhibitor umbralisib in patients with relapsed/refractory marginal zone lymphoma in a phase II study that was presented at the AACR Annual Meeting.
Results of the phase III ADMIRAL trial, which tested the FLT3 inhibitor gilteritinib in patients with relapsed/refractory acute myeloid leukemia, were presented at the AACR Annual Meeting.

The FDA has granted Priority Review to Celgene’s application for lenalidomide in combination with rituximab for previously untreated follicular lymphoma.
A recent study evaluated whether living in an industrial city could be an important risk factor for developing AML.

The PRECIS study looked at consolidation treatment with autologous stem cell transplantation vs whole-brain radiation therapy in younger patients with CNS lymphoma.
Although many immunotherapies for AML have been explored, none have ever been shown to reduced relapse rates.

Researchers examined the effect of early progression in a real-world setting of follicular lymphoma patients.
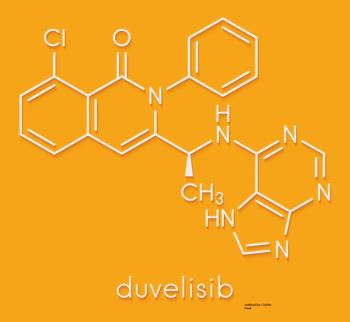
The DYNAMO study investigated the oral PI3K gamma inhibitor duvelisib in heavily pretreated indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma patients.
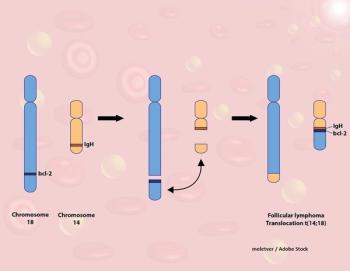
In this study, single-agent ofatumumab did not show superiority to rituximab or obinutuzumab, raising the question of whether ofatumumab should have a role in the treatment of follicular lymphoma.
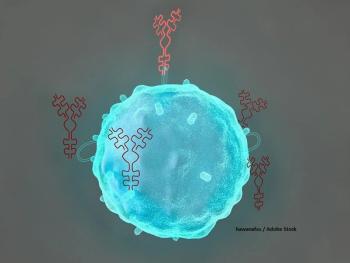
The final results of the LNH-PRO-05 study showed that a combination of antiproliferative and immunomodulatory agents with chemo had good outcomes in follicular lymphoma patients.
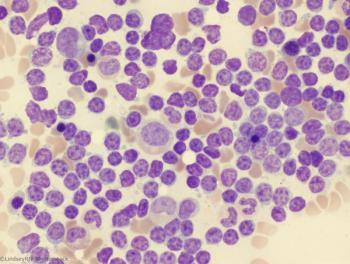
The combination of ibrutinib and nivolumab showed promising clinical response in patients with Richter’s Transformation.
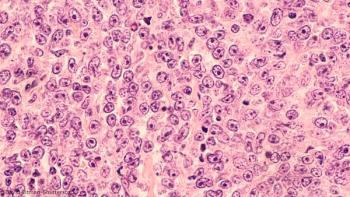
Is Aurora A kinase inhibitor alisertib superior to standard treatment protocol for peripheral T-cell lymphoma?

Dr. Copelan discusses the use of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy in non-Hodgkin lymphoma patients and how these therapies might improve upon the current standard of care.
Investigators evaluated whether AZD3463 can induce apoptosis in a dose-dependent manner in a subset of AML patients.
Researchers evaluated the primary mechanisms governing drug resistance and relapse in patients treated with crenolanib, an FLT3 inhibitor.
A retrospective study finds that younger mantle cell lymphoma patients may achieve longer PFS with AHCT consolidation.

Allogeneic transplantation was found not to improve overall outcome, in particular for patients who achieved MRD-negative status after induction.
A study investigates whether FL patients had fewer early disease progression events when assigned to treatment with obinutuzumab plus chemotherapy.

Is the continuation of maintenance rituximab beneficial post bendamustine plus rituximab treatment in FL Patients?

Guidelines for cancer screening in survivors of childhood HL may be refined based on the results of this extended follow-up study, say the researchers.