The International Lymphoma Radiation Oncology Group laid out a set of emergency recommendations for alternative radiation treatment schemes for treating patients with hematologic malignancies during the COVID-19 pandemic.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


The International Lymphoma Radiation Oncology Group laid out a set of emergency recommendations for alternative radiation treatment schemes for treating patients with hematologic malignancies during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Researchers found that the potential availability of CAR T-cell therapies for large B-cell lymphomas with lower adverse event rates that are suitable for outpatient administration may reduce the total costs of care.
AstraZeneca announced it will be conducting a global clinical trial, CALAVI, to examine the impact of adding acalabrutinib to best supportive care for patients who are severely ill with the COVID-19 infection.
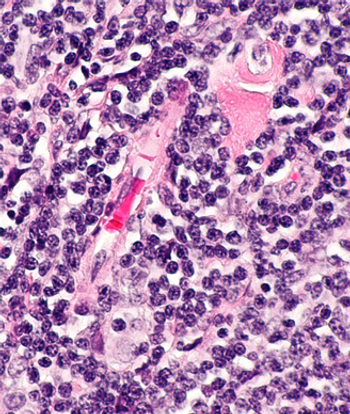
Michael L. Grossbard, MD, suggested that chemo-free regimens, including PI3K inhibitors and a more widespread use of allogeneic stem cell transplant, are being explored as treatment options in this space.
Researchers found that in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia receiving commercial ibrutinib, initial dose and dose modification during therapy did not appear to impact event-free survival or overall survival.
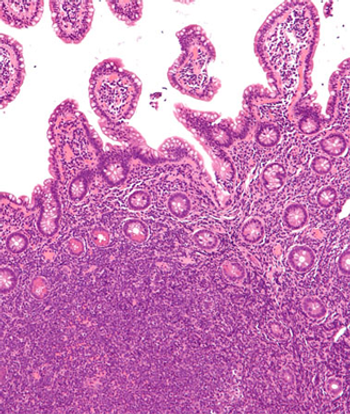
A 1-year follow-up of the phase II ZUMA-2 study found that KTE-X19 induced durable remissions in a majority of patients with relapsed or refractory mantle-cell lymphoma.

The FDA granted fast track designation to ME-401, an investigational selective oral inhibitor of PI3K delta, for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma.

A study showed that adolescents and young adults with certain types of cancers saw significant improvements in their 5-year mortality rates, while other cancer types saw little to no significant improvement among the same demographic group.

The FDA granted orphan drug designation to umbralisib based on results from the phase IIb UNITY-NHL trial cohort of patients with follicular lymphoma who have received at least 2 prior lines of therapy, including an anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody and an alkylating agent.
At the 37th Annual Miami Breast Cancer Conference, Valerie Lemaine, MD, MPH, FRCSC, told physicians what they need should know and discuss with their patients about BIA-ALCL.

Kura Oncology’s leading drug candidate, tipifarnib, was granted fast track designation by the FDA to treat adults of T-cell lymphomas.

The new guidelines provide additional guidance for healthcare providers to better recognize and diagnose breast implant-associated anaplastic large cell lymphoma (BIA-ALCL).

The FDA granted priority review to a biologics license application for tafasitamab in combination with lenalidomide for the treatment of patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.
This recommendation was based on an analysis of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma undergoing auto-HCT in which the addition of rituximab to the BEAM conditioning regimen had no impact on transplantation outcomes.
These data, in combination with durable complete responses and overall survival data, suggested that tisagenlecleucel improved health-related quality of life in adult patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma who respond to treatment.

The FDA granted a priority review to selinexor oral tablets for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, not otherwise specified, who have received at least 2 prior therapies.

The submission was primarily based on updated phase II efficacy and safety data for tazemetostat for patients with relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma who have received at least 2 prior lines of systemic therapy.

Bristol-Meyers Squibb Company announced that the FDA granted a priority review to its BLA for liso-cel to treat patients with relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphoma.

The biologic license application is supported by data from the phase II ZUMA-2 trial, which is currently assessing the CAR T-cell therapy for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma.

Researchers found that targeting BCL-W in Burkitt lymphoma and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma may not offer wide-ranging therapeutic benefit.
Patients with either relapsed or refractory non-Hodgkin lymphoma or chronic lymphocytic leukemia treated with CAR NK cells had a response without the development of cytokine release syndrome, neurotoxicity, or graft-versus-host disease.

Calibr received approval from the FDA to move forward with an investigational new drug to treat relapsed/refractory B-cell malignancies with a switchable CAR T-cell therapy.
The study is evaluating the oral inhibitor for patients with relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma.

Researchers indicated that a lack of understanding of the mechanism and efficacy of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors is the major barrier for prescription of these inhibitors in Chinese tumor treatment-related departments.
The data was presented at the EHA-EBMT 2nd European CAR T-Cell Meeting, which took place on January 30, 2020 in Barcelona, Spain, and showed encouraging signs of a manageable safety profile in adults with relapsed/refractory DLBCL.