In this study, patients with advanced urothelial carcinoma saw worse outcomes with proton pump inhibitor (PPI) use when treated with atezolizumab, compared with those who were not treated with PPIs.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!

ADC Continues to Show Clinical Activity in Heavily Pretreated Metastatic Urothelial Carcinoma
Durvalumab Monotherapy, Combination Fail to Improved OS in Metastatic Urothelial Carcinoma

In this study, patients with advanced urothelial carcinoma saw worse outcomes with proton pump inhibitor (PPI) use when treated with atezolizumab, compared with those who were not treated with PPIs.
In this study, antibiotic use was consistently associated with worse survival outcomes in patients with urothelial carcinoma treated with atezolizumab, but not chemotherapy.

The FDA approved avelumab for the maintenance treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma that has not progressed with first-line platinum-containing chemotherapy.
The trial is evaluating pembrolizumab in combination with chemotherapy for the first-line treatment of patients with advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma.
The study, titled OLYMPUS, suggested that primary chemoablation of low-grade upper tract urothelial cancer with intracavitary UGN-101 resulted in clinically significant disease eradication.
In a webinar, a multidisciplinary team from Duke Cancer Center came together to discuss the differences in treating patients with genitourinary cancer as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic.
A recent study found that switch maintenance therapy after first-line platinum-based chemotherapy led to higher objective response rates and longer progression-free survival for patients of urothelial cancer.
Researchers reported updated findings of infigratinib in upper tract urothelial carcinoma and urothelial carcinoma of the bladder, supporting the development of phase III studies in this setting.
Researchers reported on the incidence and outcomes of the SARS-CoV-2 infection, which has been linked to COVID-19, in patients with cancer who were treated at a tertiary cancer institution in Wuhan, China.

Biomarkers of carcinogens, including several with a strong link to bladder cancer, were found to be present in the urine of e-cigarette users.

This study provides the first evidence of the urinary TERT promoter mutations to be used as simple and cost-effective non-invasive biomarkers for the early detection of bladder cancer.

The FDA granted breakthrough therapy designation to enfortumab vedotin based on results from the dose-escalation cohort and expansion cohort A of the phase Ib/II EV-103 trial.
The FDA approved enfortumab vedotin-ejfv (Padcev)-the first drug to treat adult patients with locally advanced or metastatic urothelial cancer who have received prior treatment with a PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor and platinum-containing chemotherapy.

The FDA approved pembrolizumab for the treatment of patients with BCG–unresponsive, high-risk, non-muscle invasive bladder cancer with carcinoma in-situ with or without papillary tumors who are ineligible for or chose to not undergo cystectomy.
The study found that patients who were randomized to receive avelumab and best supportive care lived significantly longer than those who only received best supportive care.

The FDA granted accelerated approval to enfortumab vedotin-ejfv for the treatment of adult patients with locally advanced or metastatic urothelial cancer.

The anti-PD-1 therapy was recommended as a treatment for certain patients with high-risk, non-muscle invasive bladder cancer.

The FDA has granted priority review to a supplemental biologics license application for pembrolizumab for the treatment of patients with BCG-unresponsive, high-risk, non-muscle invasive bladder cancer.
Patients with endometrial cancer pose a very high risk of dying from cardiovascular diseases in the year after diagnosis, suggesting the necessity of early involvement of cardiologists for these patients.
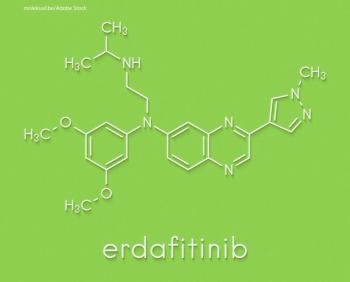
Erdafitinib is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor of fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 through 4 and was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration earlier this year as a second-line treatment for patients with locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma with susceptible FGFR3 or FGFR2 genetic alterations.

A new study found a biopsy of a single metastasis may be enough to help oncologists tailor a treatment that targets all of a patient’s tumors.

A new agent that targets Nectin-4, a protein found in 97% of urothelial cancers, may be an option for patients with locally advanced or metastatic forms of urothelial cancer.

Dr. Balar highlights promising evidence on the potential benefits of the use of immunotherapy in the advanced bladder cancer setting.
The updates to the guidelines reflect recent advances, including recommended immunotherapies and changes in tumor staging.

Cancer Network spoke with Dr. Petros Grivas about emerging immunotherapy approaches for the treatment of advanced urothelial cancer.