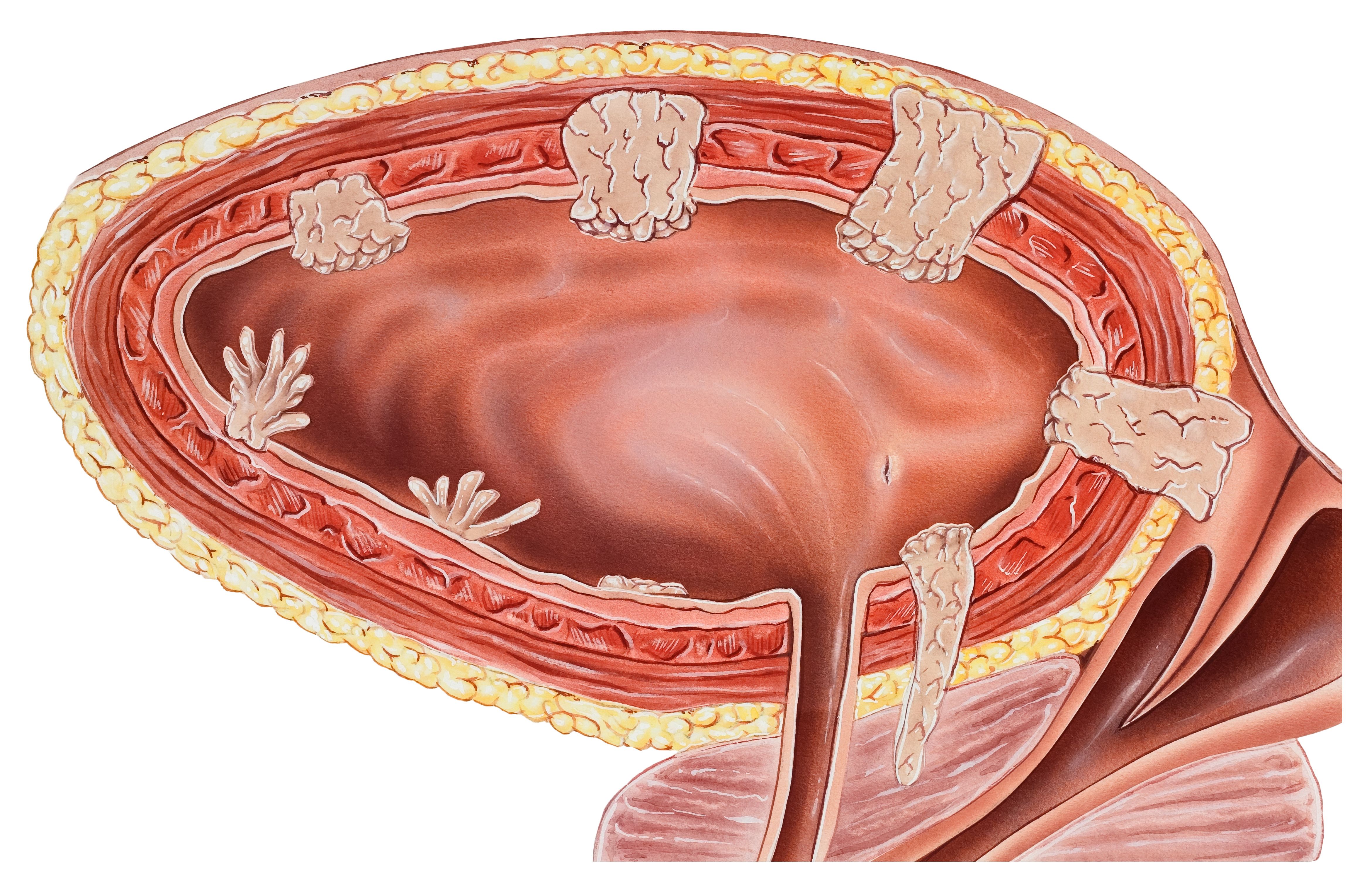
Bladder Cancer
Latest News
Video Series

Latest Videos
Podcasts
CME Content
More News
More than 80% of patients in cohort B of the QUILT-3.032 study avoided cystectomy at 36 months after treatment with nogapendekin alfa plus BCG.
A clinically meaningful and statistically significant pathologic complete response rate advantage was seen with the enfortumab vedotin combination.
The intravesical MVR-T3911 treatment did not lead to any dose-limiting toxicities in patients with high-risk, BCG-unresponsive non-muscle invasive bladder cancer.
During treatment with TARA-002, there were no grade 3 or higher TRAEs, and TRAEs did not lead to any treatment discontinuations in patients with BCG-naïve NMIBC.
A 6-month CR rate of 62% was observed with detalimogene voraplasmid in treating patients with BCG-unresponsive non–muscle invasive bladder cancer.
HRQOL scores were similar among patients who received a radical cystectomy or bladder persevering therapy for non-muscle invasive bladder cancer.
Investigators are currently assessing the safety and preliminary activity of AVZO-103 among patients with advanced solid tumors in a phase 1/2 trial.

Results from the KEYNOTE-905 trial led to the approval of pembrolizumab/enfortumab vedotin in muscle invasive bladder cancer.
Most patients with BCG-unresponsive NMIBC treated with detalimogene voraplasmid did not experience TRAEs, and only 1.6% experienced dose interruptions.

The FDA agreed that data from the UTOPIA trial, with UGN-103 demonstrating a 77.8% 3-month CR rate in patients with LG-IR-NMIBC, support an NDA submission.

Among patients with locally advanced/metastatic urothelial cancer who received at least one 2.2 mg/kg dose of BL-B01D1, the confirmed ORR was 44.1%.
Enfortumab vedotin plus pembrolizumab before and after surgery improved EFS vs surgery alone in patients with MIBC in the phase 3 EV-303 trial.
Updated results from SunRISe-4 support further investigation of the gemcitabine intravesical system plus cetrelimab in MIBC.
Data from POTOMAC support durvalumab plus BCG and induction and maintenance therapy as a new treatment option in BCG-naive, high-risk NMIBC.
New findings reveal that adding durvalumab to neoadjuvant chemotherapy does not enhance HRQOL in muscle-invasive bladder cancer patients.

Using multiparametric MRI for initial staging, then cystoscopic biopsy, improves bladder cancer-specific survival compared with transurethral resection of bladder tumor staging.

Updated results from CheckMate 274 support adjuvant nivolumab as a standard of care for patients with high-risk muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma.

The safety profile of the atezolizumab with Bacillus Calmette-Guérin in NMIBC was consistent with that of each individual agent.
Data support the intravesical mitomycin solution’s role as an innovative option for those with recurrent, low-grade, intermediate-risk NMIBC.
No toxicity-related discontinuations were seen with adjuvant radiotherapy among patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer.

Gary Steinberg, MD, compared the AE profile of the gemcitabine intravesical system for BCG-unresponsive NMIBC with other intravesical therapies.

Gary Steinberg, MD, highlights the FDA approval of the gemcitabine intravesical system and what this means for patients with BCG-unresponsive NMIBC.

In patients who refuse or are ineligible for radical cystectomy, the gemcitabine intravesical system may be given after unsuccessful BCG treatment.

Patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer with a positive Signatera test displayed a significant improvement in disease-free and overall survival.
Results from the SunRISe-1 trial showed that TAR-200 monotherapy achieved a complete response rate of 82.4% in patients with BCG-unresponsive NMIBC.