
Treatment for prostate cancer with external beam radiotherapy was found to be associated with an increased risk for development of bladder cancer when compared with radical prostatectomy.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


Treatment for prostate cancer with external beam radiotherapy was found to be associated with an increased risk for development of bladder cancer when compared with radical prostatectomy.

Measures of frailty and comorbidity failed to offer predictive information regarding complications in patients with bladder cancer undergoing radical cystectomy.
New research suggests that immune resistance in urothelial cancer may be mediated by stromal cells, which act as a source of EMT-related gene expression.
A dose-dense neoadjuvant chemotherapy regimen yielded higher response rates compared with a standard regimen in a cohort of bladder cancer patients.
A meta-analysis identified several factors that are correlated with locoregional recurrence in patients with nonmetastatic muscle-invasive bladder cancer.
Patients treated with anti–PD-1 or anti–PD-L1 inhibitors in clinical trials were successfully retreated with the inhibitors after discontinuing the treatment.

An existing body of literature shows that marital status and related social support are connected with disease outcomes.
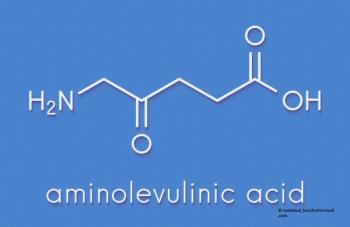
TURBT with fluorescent light source using oral 5-ALA is well tolerated in non–muscle-invasive bladder cancer.

Patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer who underwent trimodal therapy had significantly poorer survival than those who underwent radical cystectomy alone.

A new study identified several metabolites and metabolic indicators as potential biomarkers for recurrence risk in non–muscle-invasive bladder cancer.

A phase II study found that the FGFR inhibitor erdafitinib yields a good response rate and was well tolerated in patients with urothelial carcinoma and FGFR alterations.

An intravesical instillation of gemcitabine following TURBT reduced the risk of recurrence in patients with suspected low-grade non–muscle-invasive urothelial cancer.

A neoadjuvant dose-dense regimen was active and well tolerated in patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer, allowing downstaging of most patients before radical cystectomy.

Dr. Elizabeth Plimack discusses her 2018 AACR meeting presentation on recent advances in systemic therapy for bladder cancer.

Pembrolizumab offered stable or improved measures of global health status and quality of life compared with chemotherapy in patients with previously treated advanced urothelial cancer.

The FDA has granted a Breakthrough Therapy designation to the antibody-drug conjugate enfortumab vedotin for patients with locally advanced or metastatic urothelial cancer.

Differential methylation in CITED4, as measured in blood, appears to be a promising marker of bladder cancer susceptibility in women.
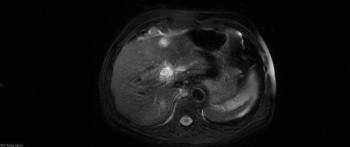
An 83-year-old man was diagnosed with multiple low-grade transitional cell carcinomas over a 6-year period. A surveillance cystoscopy in year 7 showed high-grade noninvasive papillary urothelial carcinoma in the bladder trigone. A CT urogram showed a soft-tissue mass with diffuse enhancement in the lower pole of the left kidney, concerning for malignancy.

Alterations to DDR genes were associated with improved outcomes in patients with metastatic urothelial carcinoma who were treated with immunotherapy.

In this interview, we spoke with John J. Coen, MD, a radiation oncologist who presented results at the 2018 Genitourinary Cancers Symposium of a phase II study exploring two different radiation-plus-chemotherapy combination strategies in patients undergoing bladder surgery for their tumors.

A large phase I trial offers further evidence that the anti–PD-L1 agent avelumab is generally well tolerated and results in relatively few serious adverse events.

A 67-year-old man, a former smoker, presented with gross hematuria. A CT urogram showed a bladder tumor in the anterior wall and multiple enlarged retroperitoneal lymph nodes. Two vertebral metastases were seen on a bone scan. He underwent a transurethral resection of the bladder, and the pathology report revealed muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma.

Adjuvant platinum-based chemotherapy is associated with delayed metastasis among patients diagnosed with upper-tract urothelial carcinoma, according to findings from the phase III POUT trial.

Long-term follow-up showed that atezolizumab remained well tolerated over more than 3 years, with durable clinical benefit in metastatic urothelial carcinoma.

A newly developed clinical model can predict overall survival for patients diagnosed with advanced bladder cancer who are treated with atezolizumab.