A reduction in testosterone levels in the first year of ADT correlates with improved survival in prostate cancer patients being treated for biochemical failure.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


A reduction in testosterone levels in the first year of ADT correlates with improved survival in prostate cancer patients being treated for biochemical failure.
Phase II study results found that half of patients with relapsed or refractory urothelial carcinoma responded to treatment with pazopanib and paclitaxel.

In this interview we discuss the changing landscape of systemic therapies for the treatment of bladder cancer.
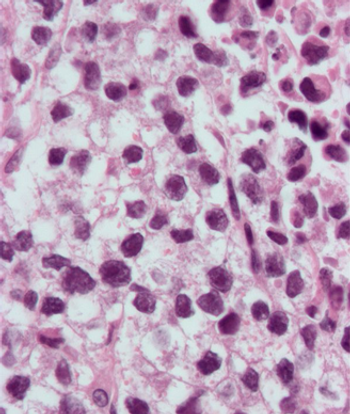
A 37-year-old man presents with a mass in the left testicle. What is your diagnosis?

As part of our coverage of the ASCO GU Cancers Symposium, we discuss decision-making in the management of patients with early-stage prostate cancer.
The 4Kscore blood test has been shown to accurately detect the presence of high-grade prostate cancer, according to a study presented at ASCO GU.

Two clinical factors may predict PSA response to cabazitaxel in men with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer.
Patients with bladder cancer derived an overall survival benefit from the use of adjuvant chemotherapy compared with observation.
Metastatic renal cell carcinoma patients with an elevated neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio at baseline had inferior outcomes compared to those with a low ratio.

Intermediate-risk prostate cancer patients managed with surveillance had worse outcomes compared with low-risk prostate cancer patients managed with surveillance.

High-dose radiation therapy did not improve overall survival compared with the standard dose in stage II localized prostate cancer, but did show some benefits.
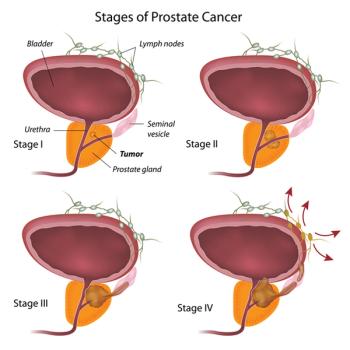
This slide show features pathology slides and PET/CT scans of prostate cancer, as well as various images of bone lesions from metastatic disease.
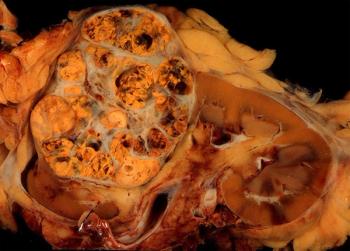
This slide show features various images of papillary, clear cell, chromophobe, and tubulocystic renal cell carcinoma.
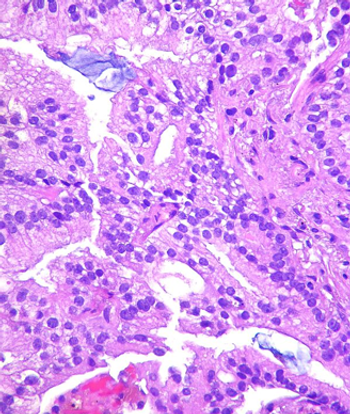
A large retrospective analysis suggests the number of patients diagnosed with intermediate- and high-risk prostate cancer has increased since 2011.
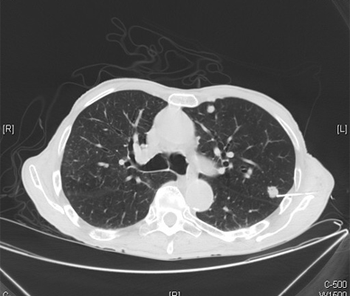
Levels of AR-V7 in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer patients could guide physicians to treat with either taxanes or enzalutamide/abiraterone.

Patients with a history of testicular cancer had a fivefold higher risk of developing aggressive prostate cancer when compared with those with no history of testicular cancer.
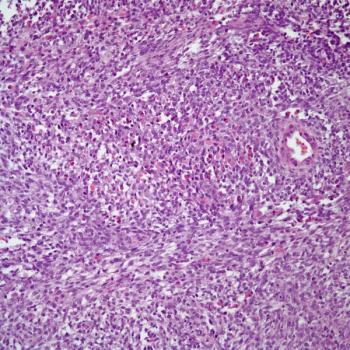
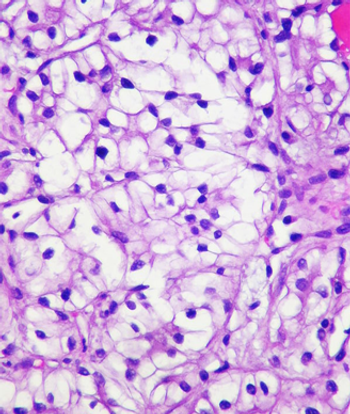
A 54-year-old man is found to have an enlarged prostate. Based on the biopsy shown, what is your diagnosis?

An 8-year analysis confirmed that adding radiotherapy to androgen deprivation therapy in prostate cancer improved patient overall survival by more than a year.

This article summarizes the existing literature on use of radiotherapy for node-positive prostate cancer, as well as the associated outcomes.

We are in urgent need of a randomized trial comparing radiation plus ADT vs ADT alone for men with node-positive prostate cancer.

Despite the lack of level 1 evidence, retrospective studies support the need for appropriate local treatment, even in the context of node-positive disease.
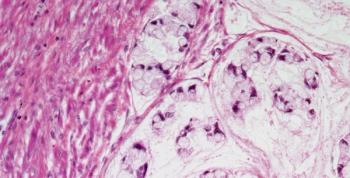
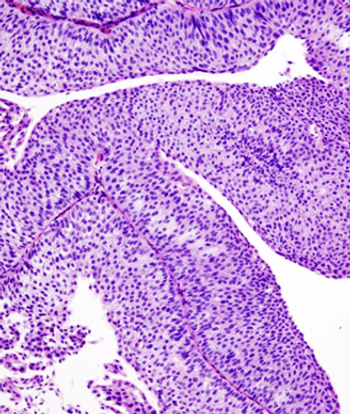
A 72-year-old man is found to have a bladder mass. After further evaluation, a biopsy is performed. What is your diagnosis?

A targeted magnetic resonance/ultrasound fusion–guided biopsy technique produced better results than a standard biopsy for detecting high-risk prostate cancer.

A urine test (CellDetect) was able to detect disease recurrence in bladder cancer patients, with a reported sensitivity of 84.4% and specificity of 82.7%.
Active surveillance is effective and yields good outcomes in patients with clinical stage I testicular cancer who underwent orchiectomy.