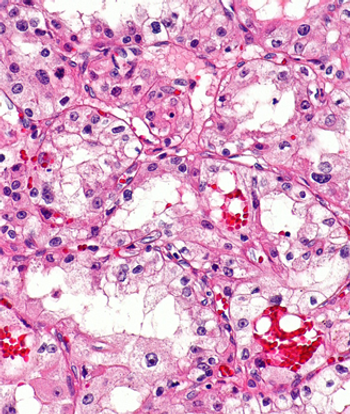
Among patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma who had undergone nephrectomy, patients with diabetes were found to have a significantly decreased cancer-specific and overall survival.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


Among patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma who had undergone nephrectomy, patients with diabetes were found to have a significantly decreased cancer-specific and overall survival.

Immediate adjuvant cisplatin-based combination chemotherapy after radical cystectomy in patients with transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder significantly increased progression-free survival, according to the final results of the EORTC 30994 trial.

When relapse occurs in patients with germ cell tumors, two salvage treatment paradigms exist: standard-dose chemotherapy, or high-dose chemotherapy with autologous stem cell rescue.

Upfront surgery allows for greater freedom to use all secondary treatment options for local and distant control, including adjuvant radiotherapy and ADT, thereby hopefully obviating the significant adverse quality-of-life sequelae from salvage surgery and brachytherapy for local relapse.

Under current conditions for patients with newly diagnosed node-positive prostate cancer, the benefits of surgery, if any, are highly unlikely to outweigh the known harms--less is still more.

Patients with renal cell carcinoma who had low preoperative levels of serum cholesterol were found to have worse survival, according to the results of a recent study.

While seven drugs have been approved for clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) since 2005, the most appropriate systemic therapy for non-clear cell renal cell carcinoma (nccRCC) is unknown.
Results of a combined analysis of SWENOTECA studies showed that surveillance remains a good option for patients with stage I seminoma testicular cancer.

Researchers have demonstrated the ability to detect AR-V7 in circulating tumor cells of prostate cancer patients with primary resistance to enzalutamide and abiraterone.
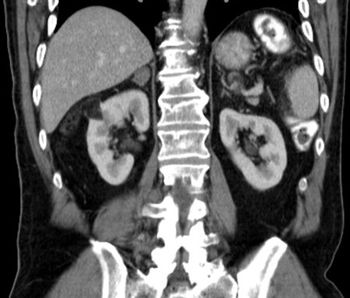
A reduced estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) was found to be associated with a significantly increased risk for renal and urothelial cancer, according to the results of a recently published study.

As part of our coverage of the 2014 American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting, we discuss some of the immunotherapy treatment options for urological cancers.

High-dose interleukin-2 remains an important treatment for patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma, producing durable responses even in those patients with chronic renal insufficiency, according to a recent study.

A large study shows that prostate cancer patients who had a PSA-based relapse could delay androgen deprivation therapy until symptoms presented, without affecting long-term survival.

While the multifunctional role of steroid hormones in prostate cancer and men’s health was recognized early, the apparent clinical benefit afforded by ADT tipped the scales in favor of androgen deprivation in men with advanced prostate cancer.

Are there ways in which testosterone administration may be beneficial? Basic science and a number of clinical experiences have suggested for years that steroid hormones may have bifunctional roles.

Researchers at the Moffitt Cancer Center have created a computational model to simulate the bone metastasis process and to predict the outcomes of specific prostate cancer therapies.

This review examines the relevance of a translational framework for studying therapeutic androgens in prostate cancer.

An increased intake of vitamin A may result in a decreased risk for bladder cancer, according to the results of a meta-analysis.
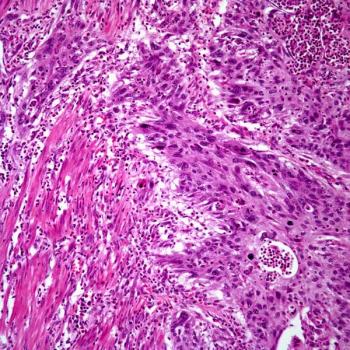
Neoadjuvant treatment with dose-dense methotrexate, vinblastine, doxorubicin, and cisplatin was well tolerated and should be considered a reasonable option for patients with muscle-invasive urothelial cancer, according to a new study.
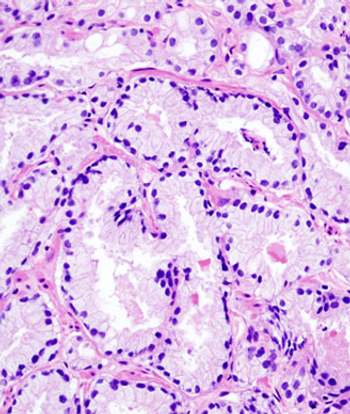
Low testosterone levels may indicate disease worsening in men diagnosed with low-risk prostate cancer who are being evaluated by active surveillance, according to a new study.
In a recent study, the drug tadalafil (Cialis) did not improve erectile function in men undergoing radiation therapy for prostate cancer.

Results from two large cohorts indicated that increasing blood pressure levels were associated with an increased risk for developing kidney cancer among both men and women.

Patients with localized prostate cancer treated with primary androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) without radiation therapy or surgery derived no survival benefit, according to the results of a large study.

The addition of gemcitabine to a cisplatin- and ifosfamide-containing drug regimen resulted in a complete response rate of greater than 50% in patients with relapsed metastatic germ cell tumors, results of a phase II study indicated.

There is no question that radiopharmaceuticals have a role in the management of patients with metastatic bone disease. There is also no question that fractionated external beam radiotherapy (EBRT) is highly effective and generally well tolerated when delivered with large open or focal fields.