
The anti-RANKL antibody denosumab is more effective for preventing bone metastasis in men with high-risk castration-resistant prostate cancer compared with low-risk disease, according to results of a new study.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!



The anti-RANKL antibody denosumab is more effective for preventing bone metastasis in men with high-risk castration-resistant prostate cancer compared with low-risk disease, according to results of a new study.

Abiraterone acetate in combination with prednisone delays pain progression as well as health-related quality of life compared with prednisone alone in prostate cancer patients, a new study shows.

In a phase III trial, ipilimumab increased the overall survival of men with advanced castration-resistant prostate cancer when used with a single dose of radiotherapy by 1.2 months, but the results were not statistically significant.

The results of the study comparing Aveo’s tivozanib to sorafenib for the treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma showed no improvement in overall survival, the basis for the FDA’s rejection of the company’s new drug application earlier this year.

There will always be patients who are either not surgical candidates or who refuse radical cystectomy, but in all other cases radical extirpative surgery should be the preferred management for patients with HGT1 disease who fail to respond to intravesical bacillus Calmette-Guérin therapy.

Decades of experience now exist to support the use of chemoradiotherapy in the treatment of muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Chemoradiotherapy for T1 tumors that recur following bacillus Calmette-Guérin therapy is promising and provides an important curative alternative for those unable or unwilling to undergo radical cystectomy.
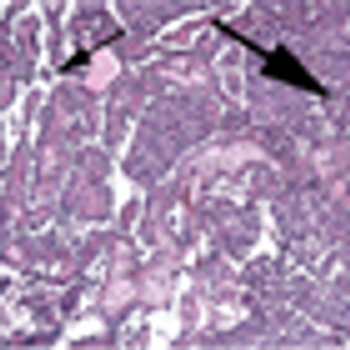
The patient is a 66-year-old male who presented to his primary care physician with a 3-week history of painless gross hematuria. He underwent a renal ultrasound that showed a left kidney mass.

A head-to-head comparison of pazopanib and sunitinib for the treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma showed that the two drugs resulted in similar progression-free survival, but also indicated that pazopanib may have a favorable safety profile.

Researchers have now identified a 3-gene signature that could indicate whether a particular early-stage prostate cancer is indolent. The test relies on a tissue sample, a PSA test, and a histology assessment.

Shift work is positively associated with higher levels of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels in men between the ages of 40 and 65, according to results of a new study.

Prostate tumors may not readily evolve from low to high grade, according to a new study. The results have important clinical implications for patients and clinicians when choosing active surveillance or treatment.

The long-term follow-up of the Prostate Cancer Prevention Trial confirms that finasteride reduces the risk of low-grade prostate cancer by one-third, but there were no significant survival differences between the two study arms.
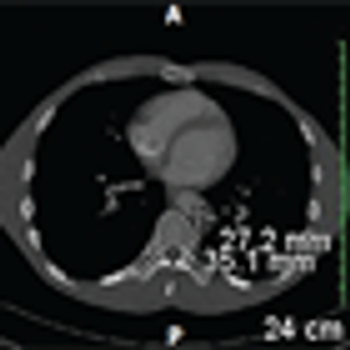
A 22-year-old man presented to the emergency department with a 5-cm painful testicular mass that had increased in size over the previous month. Tumor markers were drawn and an inguinal orchiectomy was performed.

Surgeons saw advantages in robotic, over laparoscopic, ultrasound probes during robotic partial nephrectomy, and similar perioperative outcomes and margin rates.

At the 2013 ASCO meeting, investigators of a large Danish study have concluded that surveillance alone following surgery for stage I seminoma is sufficient, sparing patients in this setting from the unnecessary expense and associated toxicities of chemotherapy and radiation treatment.

Dr. Bruce Roth, Siteman Cancer Center, spoke at the 2013 ASCO meeting about topics in seminoma. Here he discusses recurrence, relapse, and seminomatous vs nonseminomatous testicular cancer.

Dr. Bruce Roth, Professor of Oncology in the Division of Medicine at Siteman Cancer Center, Washington University at St. Louis, spoke at the 2013 ASCO meeting about topics in seminoma. Here he discusses the epidemiology of seminoma.

Dr. Bruce Roth discusses the large Danish study reported at ASCO (abstract 4502) that showed surveillance alone is sufficient after orchiectomy for stage I seminoma.

Dr. Bruce Roth discusses the large Danish study reported at ASCO (abstract 4502) that showed surveillance alone is sufficient after orchiectomy for stage I seminoma, focusing on its impact on post-surgery radiation therapy in this setting.

Both Internet and print-based decision aids equally helped men make important decisions related to prostate cancer screening, but did not affect actual screening rates.

Undergoing nephron-sparing surgery for small renal masses substantially reduced the risk of moderate renal dysfunction compared with radical nephrectomy, but not that of kidney failure among patients enrolled in the EORTC 30904 trial.

The ALSYMPCA phase III clinical trial, recently published, demonstrated that radium-223 dichloride was well-tolerated and resulted in an improvement in overall survival by 3.6 months compared with placebo.

Researchers have identified pathways that are important for prostate cancer growth after the tumor becomes resistant to androgen therapies.

A large and prospective study shows that a high concentration of omega-3 fatty acids is linked to a higher risk of aggressive prostate cancer.
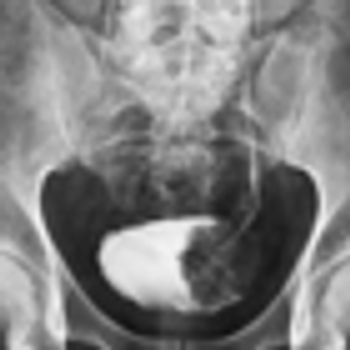
General practitioners took longer to suspect a diagnosis of bladder or renal cancer in women compared with men, according to a recent study.