
Active surveillance seems to be generally safe, yet African-American men tend to have more aggressive prostate cancers. Thus, it is imperative that we learn the characteristics and outcomes of African-American men considering surveillance.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


Active surveillance seems to be generally safe, yet African-American men tend to have more aggressive prostate cancers. Thus, it is imperative that we learn the characteristics and outcomes of African-American men considering surveillance.

There is strong evidence from longitudinal cohort studies of men with both treated and untreated Gleason 6 prostate cancer to suggest that Gleason 6 disease, when not associated with higher-grade cancer, virtually never demonstrates the ability to metastasize and thus represents an indolent entity that does not require treatment.
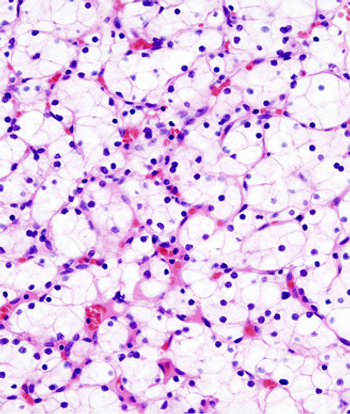
Expression of BAP1 could help identify which clear-cell renal cell carcinoma patients diagnosed with low-risk disease are the most likely to progress.

Adding a spinal or epidural painkiller to general anesthesia during prostatectomy may benefit long-term patients outcomes, according to a large retrospective study.
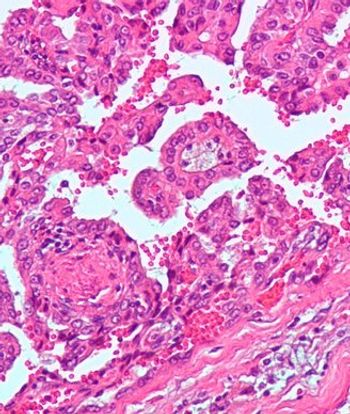
Individuals diagnosed with kidney cancer at age 46 or younger are more likely to have hereditary disease, according to a new study.

Men with early-stage prostate cancer who ate a low-fat diet supplemented with fish oil had lower amounts of pro-inflammation molecules in their blood and lower prostate tumor cell proliferation compared with men who ate a high-fat Western diet.
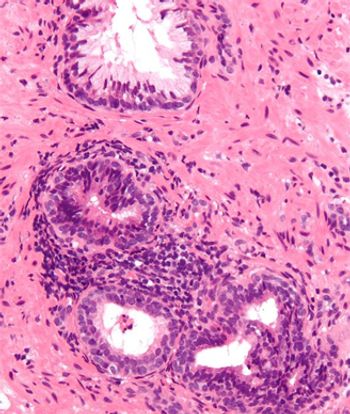
Markers of inflammation should be analyzed and reported in prostate biopsies, according to the results of a new study. Researchers found that negative prostate biopsies that had markers of inflammation were less likely to be diagnosed with prostate cancer in a subsequent prostate biopsy.

Despite the promise of proton therapy, comparative evidence has yet to definitively demonstrate its clinical benefit over other forms of contemporary radiation for prostate cancer.
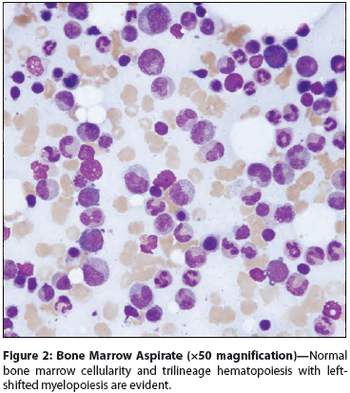
A 76-year-old woman with a history of dementia, hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and newly diagnosed squamous cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder was referred to Indiana University Medical Center after 3 to 4 weeks of hospitalization at two other hospitals.
In two phase III trials, the mTOR inhibitor temsirolimus failed to improved progression-free survival outcomes for patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma compared with other therapeutic options.
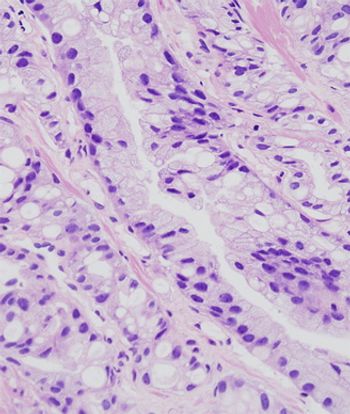
A new study shows that men who have a specific protein marker present in their prostate biopsy may benefit from close follow-up and additional biopsies as they may be at increased risk of developing cancer.
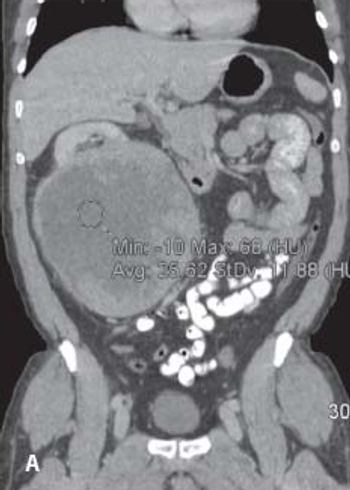
Tumor shrinkage is a valid indicator of response to VEGF inhibition among patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma when evaluated by a single radiologist observer.

The results of a recently published study on the psychological impact of prostate cancer biopsies show that men who have post-biopsy symptoms have increased anxiety, even if they received a negative diagnosis.

In this podcast, we discuss whether all male colorectal cancer patients over the age of 60 should be screened for prostate cancer.

The second generation VEGFR inhibitor axitinib did not significantly improve progression-free survival in first-line treatment of patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma compared with patients treated with sorafenib.
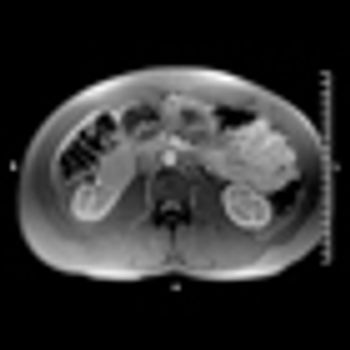
Image-guided radiofrequency ablation may be an effective alternative treatment for small renal cell carcinoma tumors, according to the results of a recent study.

Cisplatin-based chemotherapy has transformed the prognosis of testicular germ cell cancer (GCT). It has converted the chief mortal malignancy in younger men into a model for the curability of cancer.

Germ cell tumors (GCT) are an exemplar of the successful use of chemotherapy and of the successful interplay of phase II and phase III trials. The biggest contributor to cure in metastatic GCT is cisplatin-based chemotherapy, unchallenged after more than 30 years.

I have read multiple overviews of the current management of castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC). These articles have very adeptly summarized the key trials leading to a multitude of US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approvals of new agents for men with CRPC.

With the emergence of several new agents for the treatment of advanced prostate cancer, new questions have arisen regarding the optimal sequence or combination of these agents. As we await the results of ongoing and planned clinical trials to answer some of these questions directly, the decision-making process will rely heavily on considerations of side effects and patient characteristics.

In this review we will outline an approach to sequencing new therapies for metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC), with particular attention paid to the biology of CRPC.

A recent study shows that men who were overweight or obese at the time of their prostate cancer diagnosis were more likely to die from their disease compared with their healthy weight counterparts.

Results of a recent study indicate that patient progression-free survival at 3 months and 6 months was predictive of the overall survival among metastatic RCC patients treated with interferon alpha and bevacizumab.

The facts presented about screening should be tailored to the patient’s exact situation, and the patient’s values should be used to guide the final decision. For younger, healthy men, PSA screening should continue to be strongly considered.