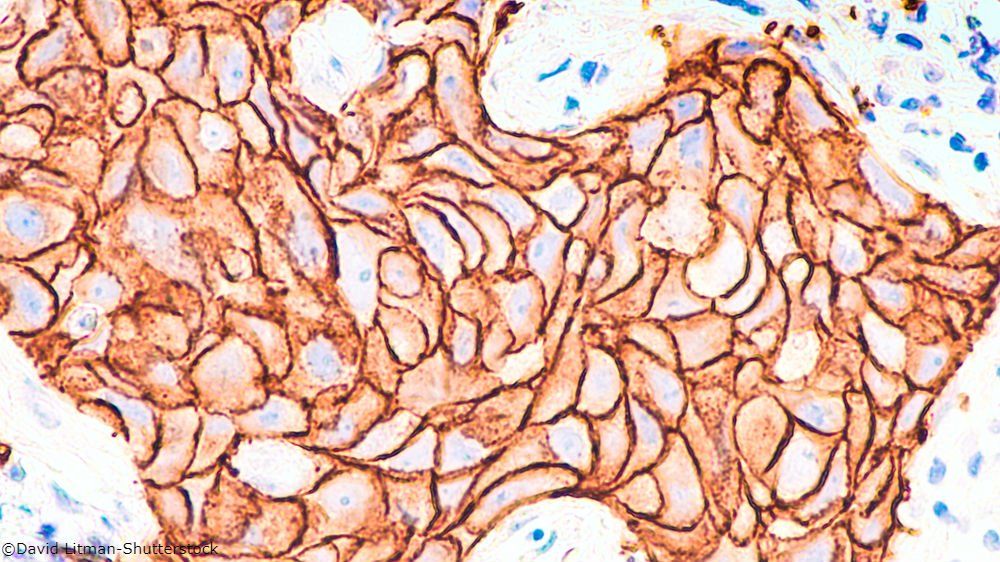
HER2-Positive Breast Cancer
Latest News
Latest Videos

CME Content
More News

The trastuzumab biosimilar ABP 980 showed noninferiority to trastuzumab in a large trial of patients with early HER2-positive breast cancer.

The HER2 TKI tucatinib plus capecitabine or trastuzumab were reasonably well tolerated and showed antitumor activity in a phase I trial of HER2+ breast cancer.

Women with HER2-positive early breast cancer achieved similar disease-free survival with 6 months of adjuvant trastuzumab compared with a 12-month duration, according to the phase III PERSEPHONE trial.

New research has found that expression of AXL is correlated with poor outcomes in patients with HER2-positive breast cancer.

A laboratory study has found that the HER2 inhibitor lapatinib used to slow HER2-positive breast cancer can actually induce tumor growth in some circumstances.

Laboratory studies suggest that mechanisms of resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy differ between the specific subtypes of HER2-positive breast cancer.

Two new studies have found that some HER2-positive and triple-negative breast cancer patients can avoid sentinel lymph node biopsy after neoadjuvant systemic therapy.

Lisinopril and carvedilol reduced cardiotoxicity in patients with HER2-positive breast cancer treated with trastuzumab and anthracyclines.

Some patients with HER2-positive breast cancer may develop an immunosuppressive phenotype based on an increase in regulatory T cells following treatment.

The addition of metronomic chemotherapy to dual HER2 blockade improved outcomes in older and frail patients with HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer.

A trastuzumab biosimilar known as SB3 showed equivalent efficacy and safety to trastuzumab itself in a phase III trial of women with early HER2-positive breast cancer in the neoadjuvant setting.

A combined approach targeting ER, HER2, and RB1 yielded promising results in terms of Ki-67 expression in women with HER2-positive, ER-positive breast cancer.

This video reviews various trials that aimed to improve outcomes or minimize toxicities among patients receiving adjuvant treatment for HER2-positive breast cancer.

Dual HER2 blockade with lapatinib and trastuzumab plus AI therapy was more effective than trastuzumab plus AI alone in HER2+, HR+ metastatic breast cancer.

Cardiac effects of pertuzumab and trastuzumab following chemotherapy in the neoadjuvant setting were limited for HER2-positive breast cancer patients.

Disease-free survival after 9 weeks of adjuvant trastuzumab and standard chemotherapy was not comparable to disease-free survival after 1 year of adjuvant trastuzumab and standard chemotherapy for women with early-stage HER2-positive breast cancer.

Adding trastuzumab to adjuvant chemotherapy did not result in improved rates of invasive disease-free survival in patients with early-stage breast cancer and low levels of HER2 expression, according to a new study.

The combination of pembrolizumab and trastuzumab showed promising clinical benefit in patients with trastuzumab-resistant HER2-positive advanced breast cancer who express PD-L1, according to a new study.

Traditional neoadjuvant chemotherapy along with dual HER2-targeted blockade yielded significantly better response rates than a novel approach using HER2-targeted chemotherapy plus HER2-targeted blockade, according to a randomized phase III trial.

A 5-year follow-up analysis showed that 1 year of extended adjuvant therapy with neratinib, given after chemotherapy and trastuzumab, can significantly improve rates of clinically relevant relapses in women with HER2-positive breast cancer.

Adding trastuzumab to anthracycline and taxane-based chemotherapy does not result in worsening of long-term cardiac outcomes in patients with node-positive, HER2-positive early breast cancer, according to a new study.

A new randomized trial found that neoadjuvant trastuzumab/pertuzumab alone yields a substantially worse rate of pathologic complete response compared with paclitaxel plus the two anti-HER2 agents for women with early HER2-positive breast cancer.

The FDA has granted Priority Review status to pertuzumab (Perjeta) for the treatment of HER2-positive early breast cancer. The FDA will review the agent in combination with trastuzumab and chemotherapy, for use in the adjuvant setting.

A new study found little difference with regard to efficacy or toxicity between two chemotherapy regimens used in combination with trastuzumab in older women with HER2-positive breast cancer. One of the regimens, containing docetaxel, was associated with a higher likelihood of completing trastuzumab treatment.

A novel ErbB inhibitor called pyrotinib was well tolerated and showed promising activity in patients with metastatic HER2-positive breast cancer, according to results of a phase I trial.