
Breast cancer tumors that are HER2-negative can spontaneously flip, with populations of circulating HER2-positive cells, suggesting treatment strategy.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!

FCGR3A Polymorphisms Predict Trastuzumab Benefit in HER2-Positive Breast Cancer
T-DM1 Offers Similar PFS, More Tolerable in Advanced HER2-Positive Breast Cancer

Breast cancer tumors that are HER2-negative can spontaneously flip, with populations of circulating HER2-positive cells, suggesting treatment strategy.

Using updated FISH guidelines yields more women with breast cancer who may be eligible for HER2-directed therapy.

Results of the I-SPY 2 TRIAL found that the neoadjuvant combination of T-DM1 plus pertuzumab resulted in a greater benefit to HER2-positive breast cancer patients compared with paclitaxel plus trastuzumab.

Combining trastuzumab emtansine with docetaxel both with and without pertuzumab yielded promising efficacy in a phase Ib/IIa study of patients with HER2-positive locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer.

A quarter of women with HER2-positive breast cancer treated with a combination of lapatinib plus trastuzumab prior to surgery had significant tumor shrinkage within 11 days.
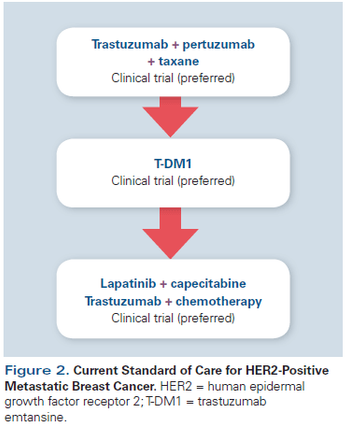
This review will summarize the current standard of care; key issues that arise when treating patients with HER2-positive disease; and developments in novel therapeutics, including small-molecule inhibitors, nanoparticles, immunotherapy, and agents targeting resistance pathways.

While we continue to be thankful for incremental gains in the treatment of our patients with metastatic HER2-positive breast cancer, much work remains in order to optimize and individualize care.

Patients diagnosed with HER2-amplified breast cancer at a younger age have a low risk of being a high-risk gene carrier, according to a new study examining susceptibility genes.

Two studies of the new HER2 selective tyrosine kinase inhibitor ONT-380 showed the drug has promising activity in HER2-positive breast cancer and especially in patients with central nervous system metastases.

T-DM1 improved survival in women with HER2-positive breast cancer, even after treatment with two or more other HER2-targeted therapies including trastuzumab and lapatinib.

Dual HER2 blockade with trastuzumab and lapatinib was no better than trastuzumab alone in producing pathologic complete responses in metastatic HER2-positive breast cancer patients in the neoadjuvant setting, according to a new study.

The use of afatinib failed to show a benefit in HER2-positive breast cancer patients with progressive brain metastases.

We acknowledge that the “more is better” approach may not always hold true. For example, preclinical data provided a rationale for combining pertuzumab with T-DM1, but recent reports suggest that this strategy may not prove more effective than single-agent T-DM1 therapy in the clinic.

The preferred status of CLEOPATRA-like regimens in the first-line HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer setting has recently been challenged by antibody-drug conjugate regimens based on ado-trastuzumab emtansine (T-DM1).

In this interview we discuss the results of the CLEOPATRA trial, which studied the effect of adding pertuzumab to docetaxel and trastuzumab on HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer.

The attainment of “no evidence of disease” after treatment for metastatic breast cancer is significantly associated with prolonged survival, according to a new study.

Adding pertuzumab to first-line therapy for HER2-positive breast cancer has been shown to yield a survival benefit, but a new analysis says adding the drug is not cost effective.

The presence of the truncated form of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (p95HER2) in circulating tumor cells is associated with poor survival in breast cancer patients.

Both chemotherapy and anti-HER2 therapy can improve survival in HER2-positive breast cancer patients with brain metastases who undergo whole-brain radiotherapy.

Using a novel imaging technique, researchers have discovered that differences in HER2 homodimers on breast cancer cells may point toward functional differences, with possible implications for metastasis and drug resistance.

[18F]FDG-PET/CT could predict response in patients with metastatic HER2-positive breast cancer treated with lapatinib plus trastuzumab.

Neoadjuvant TDM-1 was shown to be effective in treating HER2-positive, HR-positive breast cancer compared with trastuzumab, with or without endocrine therapy.

The addition of pertuzumab to trastuzumab and docetaxel offers significant improvement over other options in patients with HER2-positive breast cancer.

A randomized trial failed to show non-inferiority of 6 months of adjuvant trastuzumab compared with the standard 12 months for HER2-positive breast cancer.

MM-302 showed encouraging efficacy results and a manageable safety profile in heavily pretreated HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer patients.