
Treating advanced sarcoma with the chemotherapy agent eribulin improves overall survival compared with treatment with standard therapy with dacarbazine.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


Treating advanced sarcoma with the chemotherapy agent eribulin improves overall survival compared with treatment with standard therapy with dacarbazine.

Trabectedin failed to improve progression-free survival outcomes compared to doxorubicin as first-line therapy for advanced/metastatic soft-tissue sarcoma.
T cells that express a HER2-specific chimeric antigen receptor showed promise as a treatment for HER-2 positive sarcoma in a small phase I/II trial.

The risk of bone metastases from GISTs, though rare, should be considered during long-term follow-up of patients, especially in those with liver metastases.

In patients with high-risk localized disease, the use of systemic chemotherapy should be strongly considered to delay recurrence and/or reduce the patient’s risk of developing metastatic disease. In patients with metastatic disease, systemic chemotherapy remains the mainstay of treatment.

The unfortunate fact remains that the main chemotherapy option for patients with adult soft-tissue sarcoma is doxorubicin, a drug first identified 4 decades ago.

While the future is bright for the development and investigation of novel chemotherapeutics for treatment of soft-tissue sarcoma, investigators will need to gain better insight into the molecular drivers of pathogenesis, and give continued thoughtful consideration to clinical trial design.
Although rare, long-term recurrence of soft-tissue sarcoma is possible, and patients with retroperitoneal, very large sarcomas, or high-grade disease should undergo long-term follow-up to detect late disease recurrence.
A new study found that clinicians may be able to safely substitute cyclophosphamide for ifosfamide in the consolidation treatment of standard-risk Ewing sarcoma.
Patients with first relapse rhabdomyosarcoma treated with a chemotherapy backbone of vinorelbine/cyclophosphamide plus temsirolimus had a superior event-free survival compared to patients treated with the same backbone plus bevacizumab.

A new risk-stratification system for pediatric and young adult patients with non-rhabdomyosarcoma soft-tissue sarcomas (NRSTS) was able to effectively classify patients for the appropriate therapy.

Five extra minutes of imaging time could improve detection rates of recurrence in patients undergoing postsurgical surveillance for sarcoma.

Survivors of sarcoma have significant long-term mortality from both second cancers and noncancer-specific causes when compared with the general population, a large study showed.

A recent review clarifies the major classification changes in the current 2013 WHO classification, and factors in new genetic data that has emerged since the publication of the current volume.

Combination treatment with ifosfamide and doxorubicin for advanced soft-tissue sarcoma did not improve overall survival compared with treatment with doxorubicin alone, despite improvements in both overall response and progression-free survival.
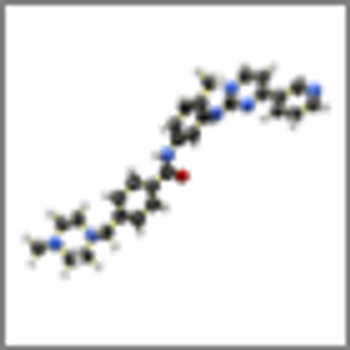
Pathologic and molecular features of gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST) were generally not correlated with outcome in a study involving adjuvant imatinib therapy following resection of the primary tumor.
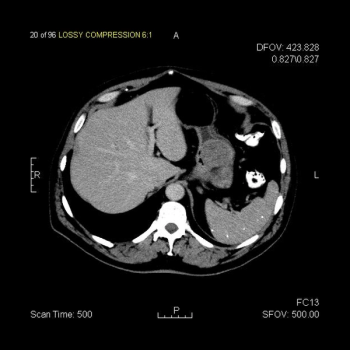
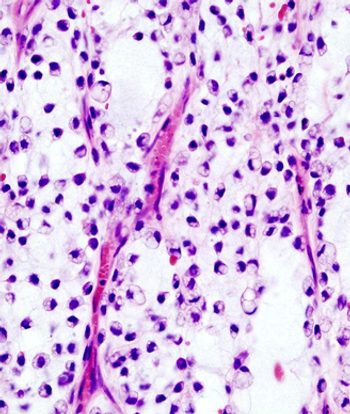
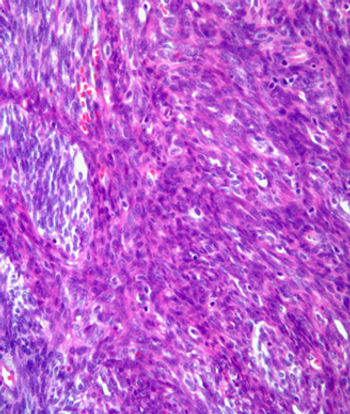
This slide show features a CT image, and pathology images of gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) arising in the stomach using H&E, CD34, and c-Kit staining.
The use of preoperative radiotherapy may be a reasonable approach to patients with borderline resectable soft-tissue sarcomas, according to the results of a retrospective study.
Single patients with soft-tissue sarcoma of the extremities had worse overall survival and were less likely to undergo several important treatment options compared with their married counterparts, according to results of a recent study.

A recent exploratory study found that GIST cells showed unexpected sensitivity to certain kinds of chemotherapy drugs not typically associated with the diseases’ treatment.
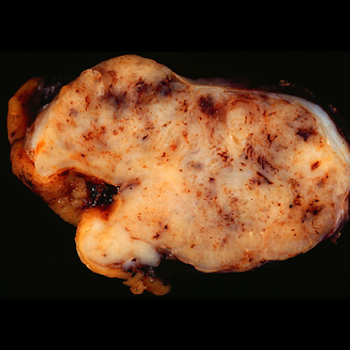
The results of a retrospective study indicated that patients with metastatic GIST who are able to achieve complete macroscopic surgical resection of their disease may be able to achieve long-term survival.
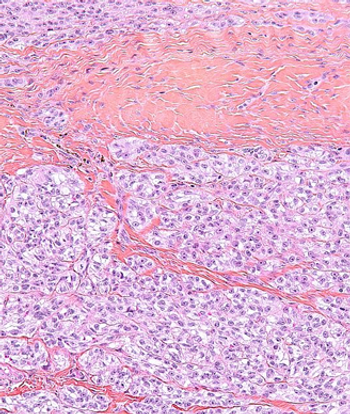
Researchers have identified several characteristics of long-term responders to pazopanib in patients with advanced soft-tissue sarcomas, including having a normal hemoglobin level at baseline.

Patients with retroperitoneal sarcomas who are unable to obtain complete resection after initial resection are left with few treatment options for palliative therapy, according to the results of a recent study.
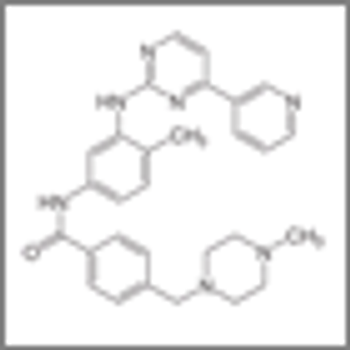
Patients with heavily pretreated metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumors were able to tolerate combined treatment with the pan-deacetylase inhibitor panobinostat and imatinib, according to the results of a small phase I study.
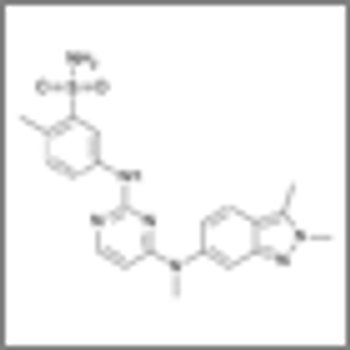
A phase II trial showed that patients with advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumors had a marginal response to pazopanib when assigned to the treatment after two or more failed therapies.