
While becoming pregnant is generally possible for younger breast cancer patients, researchers believe many women change their minds after treatment.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


While becoming pregnant is generally possible for younger breast cancer patients, researchers believe many women change their minds after treatment.
In premenopausal patients with early breast cancer, approximately one-sixth are not adequately adherent to adjuvant endocrine therapy.

Dr. Raghu Kalluri speaks with Cancer Network about the role of exosomes in cancer progression ahead of his presentation at ESMO 2018.

Dr. Luis Diaz spoke with Cancer Network about monitoring for residual disease in colon cancer ahead of his presentation at ESMO 2018.

In a first-of-its-kind study, researchers analyzed how Twitter users talk about breast cancer on the social media platform.

The relative importance of common chemotherapy side effects has shifted substantially over the last few decades, according to a new study. In general, psychosocial effects have become more important while physical effects seem less significant to patients than in the past.

The combination of ramucirumab and docetaxel prolonged progression-free survival over chemotherapy alone in patients with platinum-refractory advanced urothelial carcinoma, the first time in this setting that a regimen has improved outcomes over chemotherapy.
Nearly one quarter of breast cancer patients with small, node-negative tumors have high-risk genomic characteristics and would likely benefit from chemotherapy, according to results of a new study presented at the 2017 ESMO Congress.

The advantage with pembrolizumab has continued to improve, offering significantly better overall survival than chemotherapy in patients with recurrent, advanced urothelial carcinoma, according to the mature results of a phase III trial.

More than half of patients with metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma treated with a combination of lenvatinib and pembrolizumab responded to treatment at week 24, according to interim results of a phase I/II study presented at the 2017 ESMO Congress.

A study comparing two options for follow-up protocol after complete lung cancer resection suggests that regular CT scans after resection may not be necessary, though there may be some benefits to these additional scans.

Updated results from the KEYNOTE 059 phase II trial showed that pembrolizumab alone or in combination with chemotherapy has promising antitumor activity for patients with advanced gastric or gastroesophageal junction cancer.

The first head-to-head comparison of docetaxel and abiraterone acetate for high-risk prostate cancer patients starting long-term hormone therapy found benefit with both treatments when added to ADT. Treatment decisions may come down to specific toxicities, which differ between the treatments.

One year of combination treatment with dabrafenib plus trametinib reduced the risk for disease recurrence or death by more than half in patients with stage III high-risk BRAF V600E/K melanoma.

Weekly dose-dense chemotherapy can be delivered successfully and with lower toxicity than standard 3-weekly regimens, but it does not improve progression-free survival among patients with epithelial ovarian cancer, according to a large new study presented at the ESMO.

The addition of selumetinib to docetaxel failed to improve progression-free and overall survival in patients with KRAS-mutated locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC.

The oral PARP inhibitor rucaparib showed strong activity and an acceptable safety profile in women with high-grade, BRCA-mutated ovarian carcinoma who had previously received at least two lines of chemotherapy.

The oral PARP inhibitor niraparib yielded significantly improved progression-free survival for women with platinum-sensitive, recurrent ovarian cancer in a phase III trial.

Treatment with cabozantinib resulted in significantly improved PFS and overall response vs sunitinib for patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma.

Use of the targeted therapy dabrafenib resulted in a high overall response rate and was well tolerated in a small phase I/II study of pediatric BRAF V600-mutant low-grade glioma.

Patients with renal cell carcinoma at high risk for recurrence had prolonged disease-free survival when treated with sunitinib compared with placebo.

Adding ribociclib, a CDK4/6 inhibitor, to letrozole significantly improved progression-free survival in postmenopausal women with advanced, HR-positive/HER2-negative breast cancer.

A large percentage of patients with metastatic melanoma in Europe may not have access to innovative medicines used to treat the disease, according to the results of a survey.

The use of the PD1 inhibitor nivolumab appeared to be feasible and safe in a small study of patients with untreated, stage I–IIIa non–small-cell lung cancer.

Patients with working memory dysfunctions and depression may be more likely to be nonadherent to oral cancer therapies, according to the results of a study presented at ESMO.
A new study suggests that expression of the enzyme thymidylate synthase can be used as a predictive marker for lung cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy.
The MAGRIT trial showed no benefit with the recMAGE-A3 + AS15 cancer immunotherapeutic compared with placebo in completely resected, MAGE-A3-positive NSCLC.
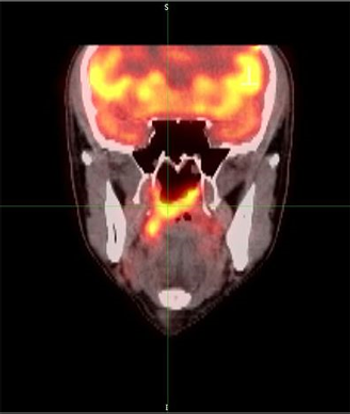
In patients with recurrent or metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, afatinib better delayed cancer progression compared with methotrexate, according to results presented at the 2014 ESMO Congress.

Rolapitant added to granisetron/dexamethasone helped prevented chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting in patients treated with cisplatin-based chemotherapy, according to a study at the ESMO 2014 Congress.
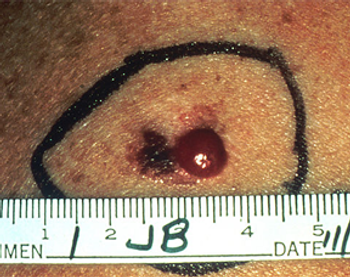
Combining BRAF and MEK inhibitors resulted in better response, PFS, and overall survival compared with a BRAF inhibitor alone in BRAF-positive melanoma patients, according to results presented at the 2014 ESMO Congress.