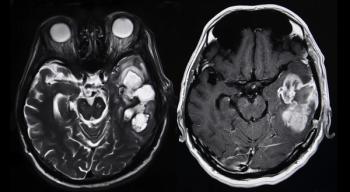
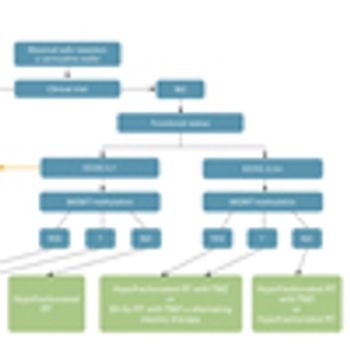
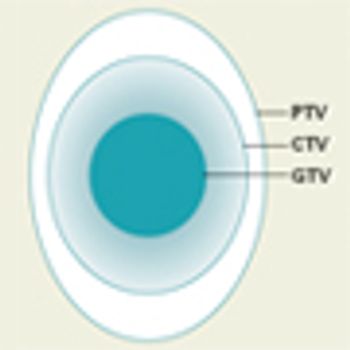
MGMT Methylation a Survival Biomarker in High-Risk Low-Grade Gliomas?
These are the first data to highlight the prognostic value of MGMT methylation beyond the IDH1/2 mutation status test currently used to help predict glioma patient survival outcomes.