
As part of our coverage of the 2014 American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting, we discuss how molecular diagnosis in medulloblastoma affects clinical decision-making.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


As part of our coverage of the 2014 American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting, we discuss how molecular diagnosis in medulloblastoma affects clinical decision-making.
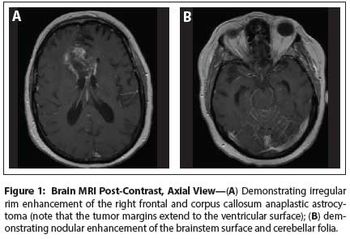
The patient is a 58-year-old woman who was diagnosed at an outside hospital with a World Health Organization (WHO) grade III non–contrast-enhancing right frontal anaplastic astrocytoma, with spread into the genu of the corpus callosum.

Significant progress has been made in defining molecular signatures in diffuse gliomas. The clinically significant genetic alterations identified to date probably represent the tip of the iceberg, since new, potentially significant biomarkers are continuously described.
We review the current data regarding the prognostic and predictive value of IDH mutation and 1p/19q codeletion in gliomas. We also discuss possible management algorithms using these biomarkers to tailor surgical and adjuvant therapy for specific diffuse gliomas.

Results of two phase III trials, presented at ASCO, on the addition of bevacizumab (Avastin) to standard therapy in newly diagnosed glioblastoma found that the drug added no benefit.

A turning point in therapy followed the observation that patients with AO tumors with chromosome 1p and 19q codeletion had better outcomes when treated with irradiation and PCV than did non-codeleted anaplastic oligodendroglioma patients.

In light of the high bar that must be met for results to be truly practice-changing, and of the long period of time before survival results are mature in an indolent disease, the primary endpoint for clinical trials in anaplastic oligodendroglial tumors needs rethinking.

Although important questions still remain regarding chemotherapy choice, sequence, and dosing, the answers to which will require additional large phase III trials, radiotherapy alone is no longer appropriate therapy for 1p/19q codeleted anaplastic oligodendrogliomas.
The combination of whole-brain radiation therapy and the EGFR inhibitor erlotinib showed a promising response rate and was well tolerated in a new phase II trial of patients with brain metastases from non-small-cell lung cancer.
Higher levels of the enzyme kallikrein 6 (KLK6) are associated with glioblastoma multiforme, the most common type of brain tumor, according to a new study from researchers at the Mayo Clinic.
Researchers have identified metformin, a drug used to treat diabetes, as a way to activate a key protein that can shut down the continued self-renewal process that keeps producing new glioma cells in glioblastoma patients.

Of particular relevance for clinicians is the possible recommendation of omitting concurrent chemotherapy with CSI in adults, due to the lower marrow reserves and overall lack of data for clear efficacy of concurrent chemotherapy in adults. Additional refinement of these therapeutic regimens for adult medulloblastoma awaits further advances in both the molecular prognostic associations for these tumors and the potentially exciting development of targeted therapies for specific molecular subtypes.

Here we present the history, staging system, and treatment of medulloblastoma, reviewing the prognostic value and clinical application of molecular subtyping while highlighting the differences between adult and pediatric disease.

Future studies of adult medulloblastoma should include whole genome sequencing and identification of the tumorigenic cell origin of adult medulloblastoma. Ultimately, quality prospective trials are needed in adult medulloblastoma patients in order to optimize the management of this rare and complex disease.
A new drug combination of lapatinib (Tykerb) and capecitabine (Xeloda) shrunk brain tumors in HER2-positive breast cancer patients whose cancer had spread to the brain, showing it is active as a first-line brain metastases treatment with similar efficacy to whole-brain radiotherapy.

The family of a young woman with a brainstem glioma has been haranguing her physician to continue bevacizumab treatment despite a significant decline in her functional status. How to respond?

The FDA approved a dissolvable form of everolimus (Afinitor Disperz) for the treatment of children with subependymal giant cell astrocytoma (SEGA) that cannot be treated with surgery.
The diagnosis of central nervous system (CNS) recurrence is a much dreaded outcome among breast cancer patients, and its incidence varies with disease stage and cancer subtype.

CancerNetwork speaks with Patricia S. Steeg, PhD, who has recently written a perspective in the journal Nature calling for a shift in both the types of drugs that are developed for breast cancer and in the way clinical trials are designed and executed.

The last two decades have seen the development of a variety of novel therapeutic agents that have improved prognoses for women with breast cancer.

In this issue of ONCOLOGY, Drs. Lim and Lin present a comprehensive and up-to-date review of the basic biology of breast cancer brain metastasis (BCBM) and of emerging strategies for treating this increasingly common complication of advanced breast cancer (BC) (BC is second only to non–small-cell lung cancer in the frequency of central nervous system [CNS] metastasis.)
Results from a phase II clinical trial with HSPPC-96 (vitespen), an autologous heat shock protein-peptide vaccine, have shown promise in patients with recurrent glioblastoma multiforme.
Hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy (SRT) appears to be safe and effective in preventing recurrence at resection cavities following surgical resection of brain metastasis and may spare many patients from whole brain radiotherapy (WBRT) and its adverse effects.
Researchers have reported cases of brain tumors among cardiologists and radiologists that work in cardiac catheterization laboratories. In addition to support from the literature, documenting 5 cases of brain tumors, a new study reports 4 new cases of brain malignancies, all in the left hemisphere of the brain.

The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved a portable noninvasive device, worn on the head, to treat adults whose glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) recurs or progresses following chemotherapy and radiation therapy.