
Updated Prognostic Tool Could Guide NSCLC Treatment in Patients With Brain Mets
An updated prognostic tool incorporating gene alteration data could help guide clinical management of patients with non–small-cell lung cancer.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


An updated prognostic tool incorporating gene alteration data could help guide clinical management of patients with non–small-cell lung cancer.

IDH1-mutant gliomas can affect adjacent, nonmalignant cells in ways that trigger seizures, according to research reported at the 21st Annual Scientific Meeting of the Society for Neuro-Oncology.

Computer analysis of subvisual data extracted from routine clinical MRI exams outperforms human experts at differentiating brain tumor recurrence from radiation necrosis.

In this interview we discuss findings from M12-356, an open-label, phase I, escalation cohort study of the investigational anti-EGFR antibody-drug conjugate ABT-414 for patients with EGFR-amplified recurrent glioblastoma.

Four years in the making, the new 2016 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System includes new genetically identified entities and variants, allowing more diagnostic precision, and a new “layered” approach to diagnosis.

Caring for patients with brain tumors can have marked effects on the well-being of oncology clinicians, frequently leading to burnout, and authors of an ongoing survey study aim to get a clearer picture of those impacts.

The anti-inflammatory ibudilast shows early preclinical promise against glioblastoma cell lines when combined with temozolomide, according to new research.

In this interview we discuss updates, challenges, and contributing factors associated with pediatric brain cancers.

In this interview we discuss fatigue, cognitive dysfunction, and psychiatric problems in patients with glioma and review which patients are more likely to encounter these issues.

Despite evolution of treatments and substantial improvements in survival, the self-reported health status among adult survivors of childhood cancers has not improved over 3 decades.

A recent retrospective study found that adding chemotherapy to postoperative treatment of craniospinal radiation for adults with medulloblastoma improves survival.
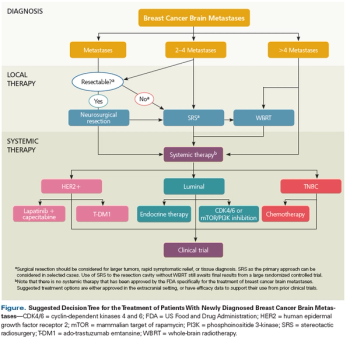
This review summarizes the most up-to-date approach to the multidisciplinary management of patients with breast cancer brain metastases.

Brain metastasis remains a relatively common and particularly devastating complication of breast cancer and has proven a particularly challenging area for therapeutic innovation.

Use of the targeted therapy dabrafenib resulted in a high overall response rate and was well tolerated in a small phase I/II study of pediatric BRAF V600-mutant low-grade glioma.
A new study is suggesting that radiomic features subjected to machine learning algorithms may be able to identify imaging signatures that defined a subset of patients with recurrent glioblastoma who may gain the most benefit from antiangiogenic therapy.

The use of an intensified treatment regimen to treat metastatic medulloblastoma in children and adolescents conferred an overall favorable survival, according to the results of a recent study. However, patients within varying subgroups and with certain biologic parameters did not have uniform outcomes.

In children with primary brain tumors who were treated with cranial radiation, cerebral volume and radiation dose may affect the rate of vocabulary development.

Vinblastine monotherapy produced outcomes similar to current therapies in children with treatment-naive pediatric low-grade glioma, and had favorable toxicity and quality-of-life profiles.

The deferral of postoperative radiotherapy is increasing among children with medulloblastoma, and this deferral of treatment was associated with worse survival.
Patients with different molecular subtypes of medulloblastoma, a common type of childhood brain tumor, have varying decline in brain function following radiation therapy for their disease.

Patients with glioblastoma who were uninsured or who had Medicaid at the time of diagnosis were more likely to be diagnosed with a larger tumor and had shorter survival times.

The underexpression of one of the homeobox (HOX) genes, HOXA11, is associated with poor prognosis in patients with glioblastoma.

In this video we discuss the use of concurrent immunotherapy and stereotactic radiosurgery for treatment of melanoma brain metastases.

Undergoing immunotherapy within a month of stereotactic radiosurgery resulted in an improved response to treatment for patients with melanoma brain metastases.

Adjuvant temozolomide chemotherapy following radiotherapy improves survival among patients with anaplastic gliomas that do not harbor 1p/19q co-deletions, according to interim results from a phase III trial.