
In most cases, PCV chemotherapy will provide an edge in outcomes over TMZ for glioma patients, primarily because of the former regimen’s use of multiple drugs and their complementary interactions.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


In most cases, PCV chemotherapy will provide an edge in outcomes over TMZ for glioma patients, primarily because of the former regimen’s use of multiple drugs and their complementary interactions.

The US Food and Drug Administration has approved dinutuximab (Unituxin) for the treatment of high-risk neuroblastoma in pediatric patients.
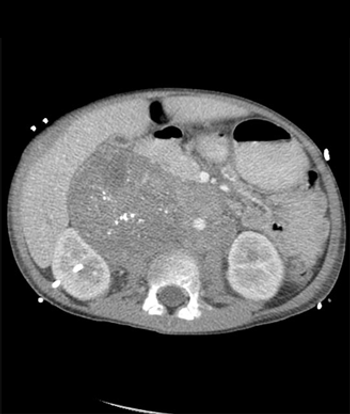
Expression of the IGF2BP1 gene was associated with more advanced tumors and decreased patient survival in neuroblastoma, suggesting its prognostic value.
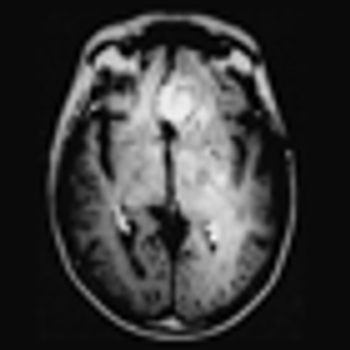
Researchers have shown that reprogramming T cells to target glioblastoma in mice resulted in control of these tumors.

A new study finds that childhood cancer survivors are at risk for pituitary hormone deficiencies after radiotherapy treatment to the head.
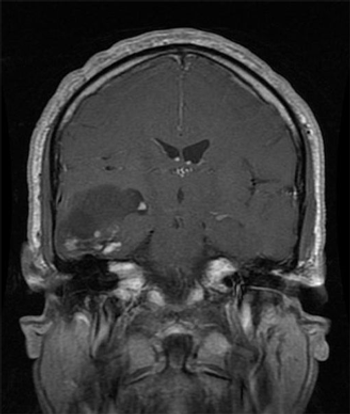
Stable, long-term survivors of low-grade glioma were able to maintain a high level of quality of life, but did experience detectable declines in certain areas.
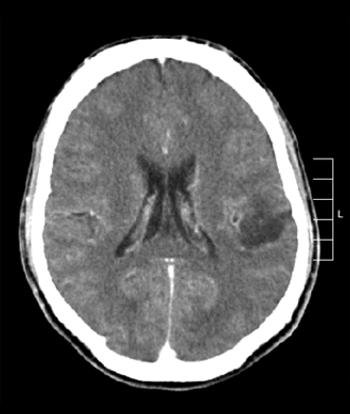
Researchers have identified two genetic characteristics that may distinguish pediatric secondary high-grade glioma from primary high-grade glioma.
A history of hormonal contraceptive use in younger women for 5 years or more was found to be associated with a possible increased risk of glioma.

As our understanding of tumor biology grows, we may identify targeted agents that can be used to treat low-grade gliomas. One such approach moving into clinical trials is the use of IDH inhibitors.
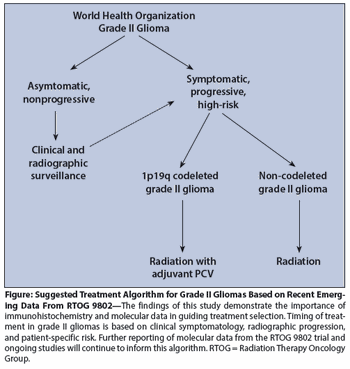
In this article, we provide a brief overview of the management of grade II astrocytomas, oligodendrogliomas, and mixed oligoastrocytomas-the three most heavily encountered and studied of the low-grade gliomas.

The recent evidence that incorporation of chemotherapeutic interventions can result in relatively long survival times for patients with low-grade glioma highlights the need to also preserve neurocognitive function and health-related quality of life in these patients.

There have been and continue to be areas of uncertainty surrounding the treatment of grade II gliomas. One in particular is the optimal timing of treatment.

New research suggests that characterizing low-grade gliomas according to molecular markers may be a more useful approach in order to guide treatment decisions.

A core set of symptoms are common across brain tumor patients and underscore the complexity of brain tumors and their management.

Depressive symptoms and impaired executive functioning, both common in patients with glioblastoma, are independently associated with shorter overall survival.

The immunotherapeutic rindopepimut with bevacizumab yielded a significant survival improvement in relapsed glioblastoma patients with a EGFRvIII mutation.

A phase I trial of an oncolytic polio/rhinovirus vaccine was safe and showed promising efficacy in patients with recurrent glioblastoma.

Treating newly diagnosed glioblastoma with “tumor treating fields” is a safe and effective therapeutic option, according to a new trial.

A combination of bevacizumab and lomustine showed promise in a randomized phase II trial of patients with recurrent glioblastoma, according to study results.
The addition of procarbazine, CCNU, and vincristine to RT in patients with low-grade glioma prolongs progression-free and overall survival vs RT alone.
As part of our Society of Neuro-Oncology annual meeting coverage, we discuss quality of life issues and neurologic rehabilitation in patients with neuro-oncologic diseases.

Prevention of CNS seeding early in the metastatic disease course using drugs with both intra- and extracranial activity will be crucial to improving outcomes in patients with breast cancer brain metastases.

Brain metastases arising from breast cancer constitute a clinically unmet need and a situation that portends a poor prognosis with few therapeutic options.
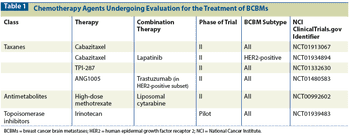
In this overview, we will review recent developments in the management of breast cancer brain metastases and current prospective trials of systemic therapies specifically for patients with breast cancer brain metastases, with a focus on novel pathway-specific therapies.

For many women, the prospect of tumors growing in their brain that may eventually impact their ability to communicate, interact, and remember is terrifying.