Neuroendocrine Tumors
Latest News

BI 764532 Earns FDA FTD in SCLC and Extrapulmonary Neuroendocrine Carcinoma
FDA Clears Chromogranin A Immunoassay in Gastroenteropancreatic NETs
Latest Videos

CME Content
More News
The addition of bevacizumab to FOLFIRI does not appear to improve overall survival over FOLFIRI alone in patients with gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine carcinoma.
Data from a retrospective study suggests that stereotactic body radiotherapy may be a suitable alternative to surgical resection for patients with primary lung neuroendocrine tumors, according to an expert from Moffitt Cancer Center.
Rolling submission with the FDA for surufatinib treatment in patients with pancreatic and extra-pancreatic neoendocrume tumors was completed and an expanded access program for the drug is currently underway for patients in the United States.

Data presented at the virtual AACR Annual Meeting 2021 showed that a phase 2 trial examining combination treatment with adavosertib plus irinotecan met its protocol-defined efficacy end point in a cohort of pediatric patients with neuroblastoma.
A study found a number of factors associated with increased recurrence risk for patients with locally advanced pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors following surgical resection, including sex, lymph node metastases, and resection of other organs with tumor involvement.
No significant benefits to progression-free survival were noted with the axitinib-plus-octreotide combination for the treatment of patients with advanced G1-2 extra-pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors.
The expert in hematology/oncology spoke about the study which evaluated the use of peptide receptor radionuclide therapy in patients with well-differentiated neuroendocrine tumors.

The Detectnet injection was approved by the FDA for the localization of somatostatin receptor positive neuroendocrine tumors in adult patients.

Cancer Network spoke with Dr. Shishir Maithel about grading and diagnosing neuroendocrine tumors and how PRRT best fits into the treatment algorithm of these tumors.
Among patients with small-bowel neuroendocrine tumors, accurate lymph node staging may require the examination of at least eight lymph nodes.
An analysis of more than 70,000 patients revealed significant differences with regard to survival between different sites of origin for neuroendocrine tumors.
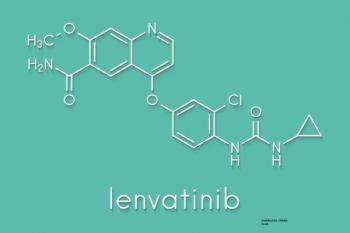
Lenvatinib offers the highest published response rate to a targeted agent for patients with advanced neuroendocrine tumors, but the agent’s precise role in this setting remains in question.
In general, NETs are considered an “immunological desert,” but a new study showed some promise for immunotherapy.

A retrospective analysis found that surgical resection and radiotherapy are linked to superior outcomes in patients with thymic neuroendocrine tumors.
Radioguided surgery using gallium 68 dota peptides offers a highly sensitive method for detecting neuroendocrine tumors.
For patients with NETs that have metastasized to the liver, high levels of serum pancreastatin are predictive of poor outcomes after treatment with TACE.
A new study suggests that the cytokine CXCL12 could be useful as a prognostic biomarker in patients with neuroendocrine tumors of the lung.

A study on pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma associated with neurofibromatosis type 1 highlights how screening for these malignancies is important.

Researchers have developed a clinical prediction model for the metastatic potential of pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma.
Intravenous Iobenguane I 131 has been approved to treat unresectable, locally advanced, or metastatic pheochromocytoma.

The US Food and Drug Administration approved lutetium Lu 177 dotatate (Lutathera) for the treatment of somatostatin receptor–positive gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors in adults.

Patients with gastrointestinal neuroendocrine tumors with carcinoid syndrome are more than twice as likely to have certain pre-existing diagnoses compared with patients without carcinoid syndrome, according to the results of a study.

Researchers are proposing the consideration of expanding criteria for liver debulking in pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors to include a threshold of greater than 70% debulking, intermediate grade tumors, positive margins, parenchyma-sparing resections, and extrahepatic metastases.
In this review, we focus on the treatment of well-differentiated early and metastatic PNETs, emphasizing current controversies, recent advances in therapy, and the multidisciplinary approach required for optimal treatment.
A study exploring the genetic underpinnings of the newly classified high-grade neuroendocrine carcinoma has found that it is a rare but aggressive tumor with a high frequency of BRAF mutations.