Researchers have identified two new panRAF inhibitors that could be used to treat patients with BRAF- or NRAS-mutant melanoma, and those who have developed resistance to BRAF inhibitors.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


Researchers have identified two new panRAF inhibitors that could be used to treat patients with BRAF- or NRAS-mutant melanoma, and those who have developed resistance to BRAF inhibitors.
Using whole-exome sequencing, researchers were able to define the genetic basis for deriving benefit from treatments that block CTLA-4 in melanoma.
The addition of sargramostim to the anti-CTLA-4 ipilimumab resulted in a significant improvement in overall survival in patients with metastatic melanoma.

In this interview we discuss a patient who experienced regression of BRAF-inhibitor-induced eruptive melanocytic nevi following concomitant addition of a MEK inhibitor.
Positive genetic risk information about melanoma may help to prompt people to discuss melanoma risk with a wider variety of family members, according to a new study.
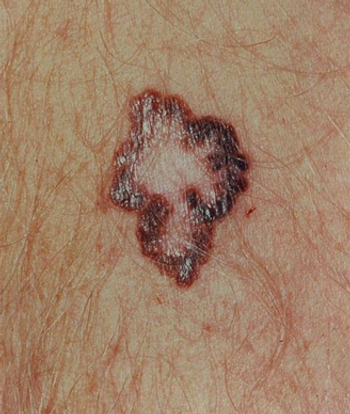
A recent study has confirmed that TERT promoter mutations are common genetic mutations in cutaneous melanoma, mutations that may be linked with poor prognosis.
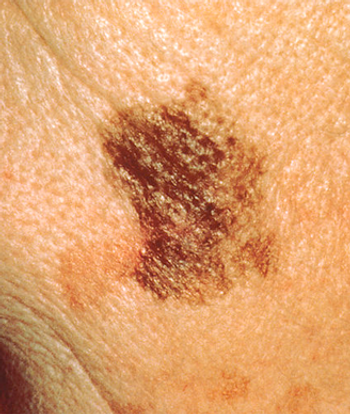
Treatment with a BRAF and MEK inhibitor resulted in modest clinical efficacy in patients whose melanoma had progressed after treatment with a BRAF inhibitor.
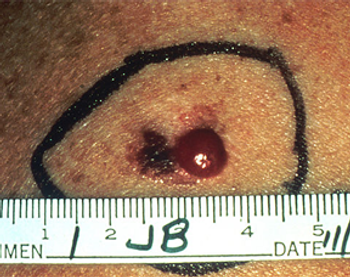
Combining BRAF and MEK inhibitors resulted in better response, PFS, and overall survival compared with a BRAF inhibitor alone in BRAF-positive melanoma patients, according to results presented at the 2014 ESMO Congress.

Pilots and cabin crews were found to have twice the incidence of melanoma and about 40% increased melanoma mortality compared with the general population.

The FDA granted accelerated approval to pembrolizumab (Keytruda) for treating patients with advanced melanoma who are no longer responding to other drugs.
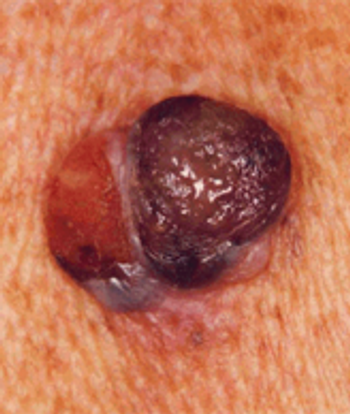
Researchers identified characteristics that may be associated with high-mitotic-rate tumors--being male, elderly, and having a history of solar field damage.
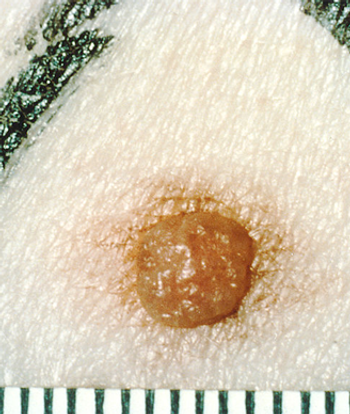
Patients taking a BRAF inhibitor are more susceptible to highly volatile melanocytic lesions that make the detection of new primary melanomas more difficult.

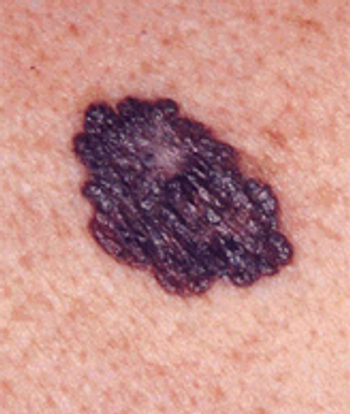
Combined treatment of BRAFV600-mutated melanoma with the MEK inhibitor cobimetinib and the BRAF inhibitor vemurafenib was safe and tolerable, according to the results of a phase Ib study.

Dr. Atkins offers his perspective on the “race” between the top two anti-PD1 drugs (Merck’s MK-3475 and Bristol-Myers Squibb’s nivolumab), and weighs in on where a new agent, pidilizumab, fits into the picture.

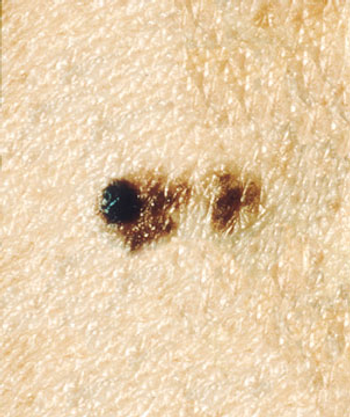
The presence of regression in melanomas with a Breslow thickness greater than 0.75 mm does not appear to be linked to a higher likelihood of sentinel node involvement, according to the results of a retrospective study.

Long-term results from a phase I study demonstrate that concurrent treatment with ipilimumab and nivolumab led to an unprecedented improvement in survival for patients with advanced melanoma.

The story of how the targeted therapies, immunotherapies, and combinations of these therapies have been developed for use in patients with advanced melanoma holds a number of important lessons for the development of agents for use in other tumor types.

Multiple abstracts on melanoma and skin cancer were reviewed at the ASCO Annual Meeting, with a focus on new treatment approaches in non-melanoma skin cancers, particularly basal cell carcinoma and Merkel cell carcinoma.
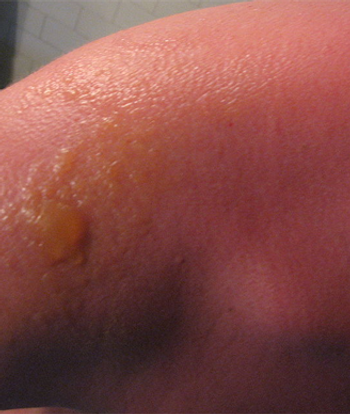
The results of a prospective study showed that the risk of developing melanoma is higher for white women with a history of strong sun exposure during childhood and adolescence, rather than adulthood.

The FDA has granted Merck’s anti-PD1 antibody MK-3475 a priority review designation for the treatment of unresectable or metastatic melanoma in patients who have previously been treated with ipilimumab.

New treatment options for melanoma continue to be developed, especially in the areas of immunotherapies and targeted agents. Oncology nurses need to be knowledgeable about the various therapies being used, indication for use, and the management of adverse events.

Oncolytic viruses are receiving more attention these days as a form of cancer treatment, and have shown promise in clinical trials. These viruses are thought not only to cause direct destruction of the tumor cells, but also to stimulate a patient's immune response.

Results of a preplanned interim analysis of the AVAST-M trial indicate that bevacizumab may have a beneficial effect on disease-free survival in patients with melanoma at high risk for recurrence.