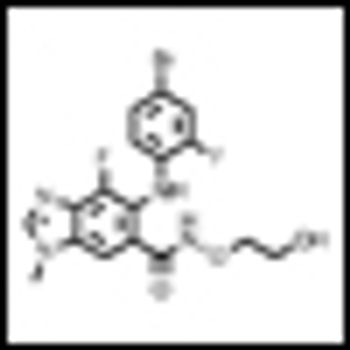
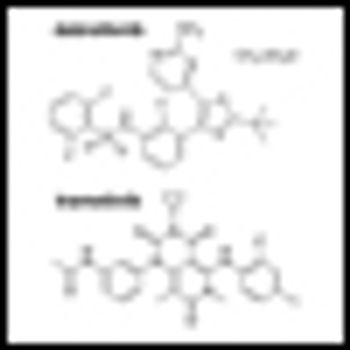
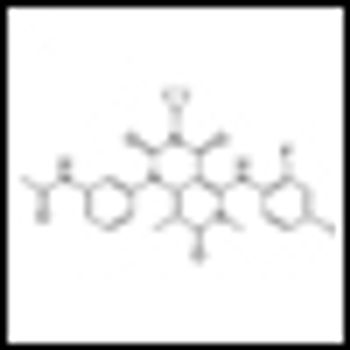
Building on the landmark studies of the immunotherapeutic agent ipilimumab just a few years back, ASCO 2013 saw the presentation of truly impressive data on two PD1 blockers, as well as noteworthy studies of other immunotherapeutic approaches to advanced melanoma.