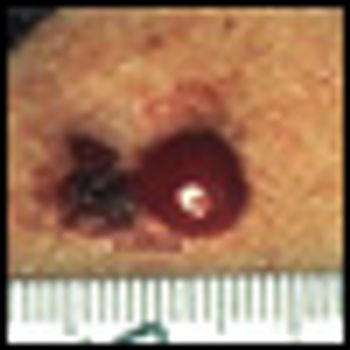
Skin cancer is the single most common form of cancer, accounting for more than 75% of all cancer diagnoses. More than 1 million cases of squamous cell and basal cell carcinomas are diagnosed annually, with a lifetime risk of more than one in five. The vast majority of skin cancers can be cured with surgery alone. Resection is the mainstay of therapy, even for skin cancer involving regional lymph nodes or, in some cases, more distant metastatic sites.