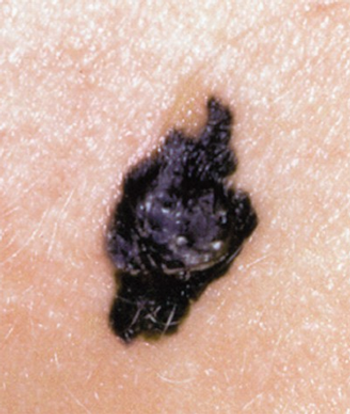
Sentinel-node biopsy for patients with intermediate-thickness melanomas increased disease-free survival and, in patients positive for nodal metastases, disease-specific survival, according to the final data from the MSLT-I study.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


Sentinel-node biopsy for patients with intermediate-thickness melanomas increased disease-free survival and, in patients positive for nodal metastases, disease-specific survival, according to the final data from the MSLT-I study.
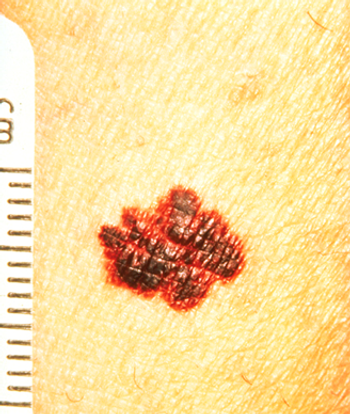
A new study found that a targeted screening and education strategy aimed at patients at high-risk for melanoma favorably affected behaviors that may reduce melanoma risk compared with a standard information-based campaign.
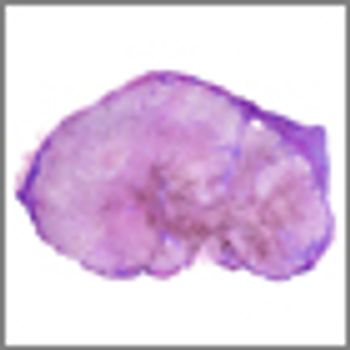
In a new study, melanoma patients who had CD30-positive T cells present in their sentinel lymph nodes were more likely to have disease progression compared with patients whose node biopsies were negative for these immune cells.

Results of a phase II study indicate that the use of 1 month of intravenous high-dose interferon alfa-2b alone for the treatment of melanoma was not superior to the standard long-term regimen, and that further study of this approach is not warranted.
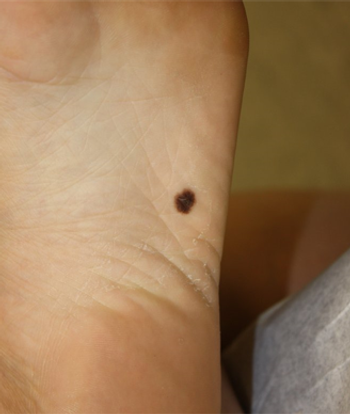
Men with a history of prostate cancer may be at increased risk for melanoma, according to data taken from two large cohort studies.
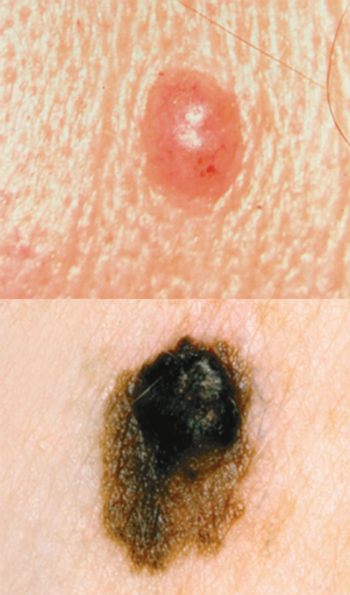
The completion of a short web-based course improved the ability of primary care physicians to diagnose and manage benign and malignant skin cancer, according to the results of a new study.
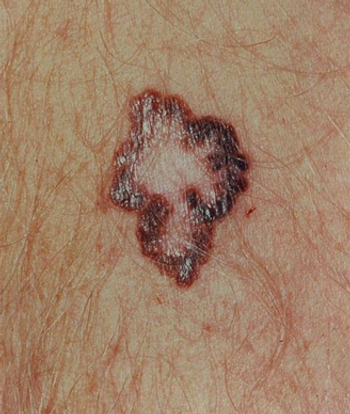

At the 10th International Congress of the Society for Melanoma Research (SMR), we spoke with Dr. Georgina Long about current targeted approaches for the treatment of advanced-stage melanoma.

Metastatic melanoma patients treated with a dabrafenib/trametinib combination experienced a 3.6-month increase in overall survival compared with patients treated with dabrafenib alone. The results were not statistically significant, partly due to the crossover design of the trial.
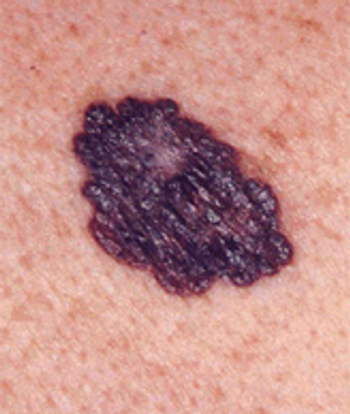
About one-third of patients with advanced cutaneous melanoma treated with MPDL3280A, an antibody against the programmed death 1 ligand (anti-PD-L1) showed a response in a phase I clinical trial.

The PD-1 inhibitor MK-3475 is continuing to show activity and long-term responses in patients with metastatic melanoma, according to results presented at the International Congress of the Society for Melanoma Research.
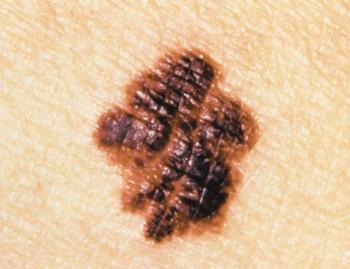
In patients with thin melanomas who are clinically node-negative, sentinel lymph node biopsy should be offered to patients with melanomas greater than 0.75 mm in Breslow thickness, according to the results of a recent study.
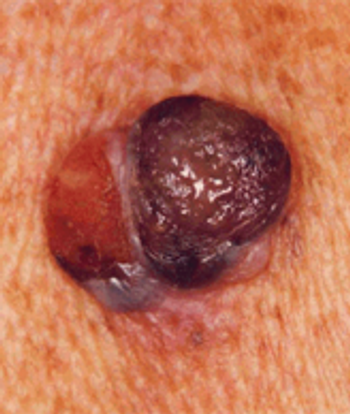
Researchers have identified a biomarker that may help physicians predict if patients with BRAF-mutant melanomas will respond to drugs designed to target BRAF.

Patients with cutaneous malignant melanoma were found to have increased their daily UV radiation dose not only while abroad or on vacation, but also on a daily basis, according to the results of a new study.

All of us treating patients with melanoma must educate our patients about the importance of participating in clinical trials with these new agents so that we can systematically validate the benefits and risks of these agents in prospectively defined patient settings.

Any minimization of therapy in the name of reducing morbidity requires careful consideration. Reducing morbidity in melanoma is certainly a laudable goal, but locoregional disease control and cure must remain our primary objectives.
A 55-year-old woman with a history of metastatic melanoma in remission for 8 years presented to the emergency department with gross hematuria. A CT scan, ordered because the patient was in menopause, demonstrated a bladder tumor.
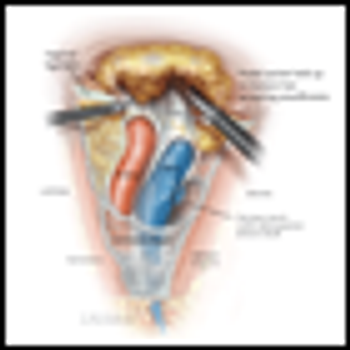
Here we review some of the most significant changes in the surgical management of melanoma that have reduced morbidity and thereby improved patient outcomes.
Patients with advanced melanoma treated with ipilimumab may be able to survive up to 10 years, according to the results of a study presented at the 2013 European Cancer Congress.

The combination of two oral targeted agents, dabrafenib (Tafinlar) and trametinib (Mekinist), has been given a priority review by the FDA for the treatment of BRAF V600-positive metastatic melanoma.

The use of GM2-KLH/QS-21 vaccination in stage II melanoma patients did not improve outcomes, according to the results of the EORTC 18961 phase III trial.

Older patients with melanoma were diagnosed with thicker melanomas, and experienced longer time to excision and a higher frequency of insufficient excision margins compared with their younger counterparts in a multicenter study in France.

A new study in early-stage melanoma patients shows that “self-eating” cells, or autophagy, can keep the cancer in check and may lead to a better prognosis.

Researchers found that circulating cell-free DNA could represent a possible predictive marker of response in advanced melanoma patients treated with dabrafenib.
Melanoma can hide in pigmented tattoos, according to a new case report describing a young man with a malignant melanoma that developed within a large tattoo.