
By exploring gene expression variables in addition to clinicopathologic variables, researchers were able to better predict which melanoma patients would have sentinel lymph node biopsy positivity.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


By exploring gene expression variables in addition to clinicopathologic variables, researchers were able to better predict which melanoma patients would have sentinel lymph node biopsy positivity.

The unprecedented advances in melanoma immunotherapy are sure to pave the way for immunotherapy development in other tumors.

Frequent consumers of citrus fruits were found to have an elevated risk of malignant melanoma.

New data suggests that cutaneous melanomas can be classified into four subtypes based on the pattern of the most prevalent significantly mutated genes.

A study of men taking PDE5 inhibitors found a small but significant increase in the incidence of malignant melanoma, though the association may not be causal.

Not surprisingly, this was a very popular topic. I’m not sure why the ASCO planners didn’t anticipate this, because I had to wait a few minutes outside the door to even get in. At one point, it was standing room only!

In this video, Dr. Martin discusses the phase III ONTRAC study, which found that the use of nicotinamide, a form of vitamin B3, reduced the incidence of non-melanoma skin cancers by 23% among a group of high-risk patients.

As part of our 2015 ASCO Annual Meeting coverage, we discussed immunotherapy combinations in advanced melanoma patients with Michael A. Postow, MD.
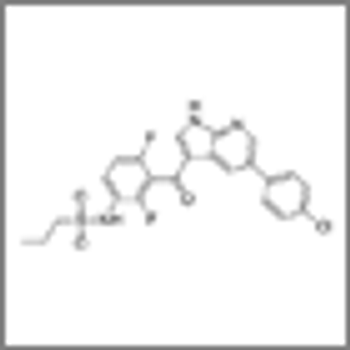
Updated results from the coBRIM trial show that a BRAF/MEK inhibitor combination continues to provide clinical benefit in BRAF-positive metastatic melanoma.

The anti–PD-1 antibody nivolumab alone or in combination with ipilimumab increased progression-free survival in treatment-naïve metastatic melanoma patients.
Due to the genetic heterogeneity observed in tumors of melanoma patients who developed resistance to BRAF inhibitors, assessing mechanisms of resistance has minimal potential to inform further treatment decisions.
Data from the KEYNOTE-001 study showed that the anti–PD-1 antibody pembrolizumab produces durable responses in metastatic melanoma patients.

Researchers have identified several key diagnostic criteria for the diagnosis of melanoma and basal cell carcinoma with reflectance confocal microscopy.

Researchers have shown for the first time that an oncolytic immunotherapy can have therapeutic benefit in patients with advanced melanoma.
MEDI4736 appears to have an acceptable safety profile and durable clinical activity, according to a new dose-escalation study.
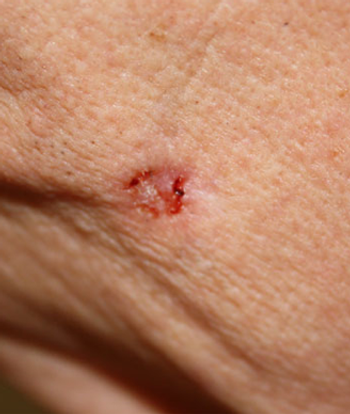
Nicotinamide, a form of vitamin B3, reduced the incidence of non-melanoma skin cancers among a group of high-risk patients, according to the ONTRAC study.
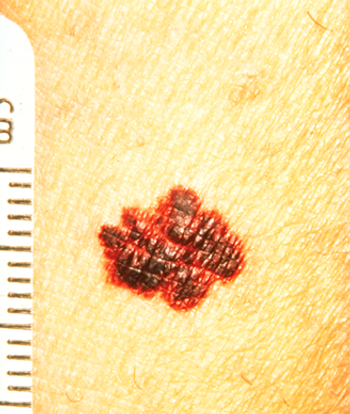
Treatment with nivolumab and ipilimumab in patients with advanced melanoma produced significantly higher rates of response and progression-free survival compared with ipilimumab alone.
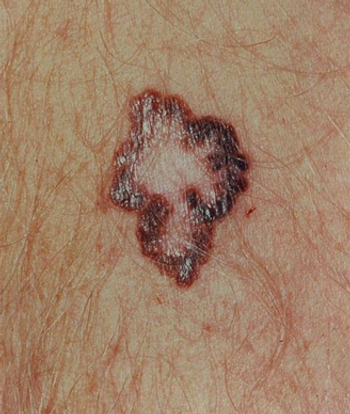
Treatment with pembrolizumab resulted in an estimated 6-month PFS rate that was almost double that of treatment with ipilimumab in advanced melanoma patients.
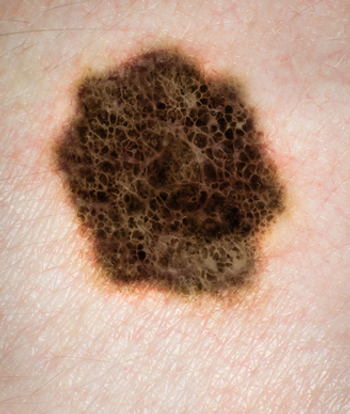
Advanced melanoma patients who progressed on ipilimumab were more likely to achieve an objective response when treated with nivolumab than with chemotherapy.

The measurement of levels of C-reactive protein (CRP) in the blood has been found to be an independent prognostic marker for survival in patients with melanoma.
Advanced melanoma patients who received front-line ipilimumab/dacarbazine had double the 5-year survival rate compared with those on dacarbazine alone.
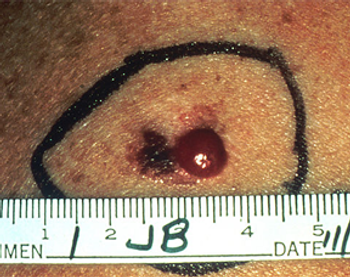
A single-institution study found that patients with melanomas of 4 mm thickness who had a negative sentinel lymph node biopsy had significantly prolonged survival.
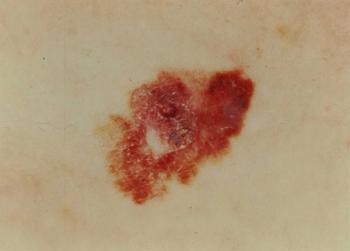
This slide show features images of melanoma, basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, as well as images of metastatic disease.

In early 2015, determining the optimal treatment regimen for a patient with metastatic melanoma remains challenging.

While the last several decades saw a lack of progress in treatment outcomes in this setting, the outlook has recently changed dramatically, driven by a deepening understanding of melanoma biology and host immunology.