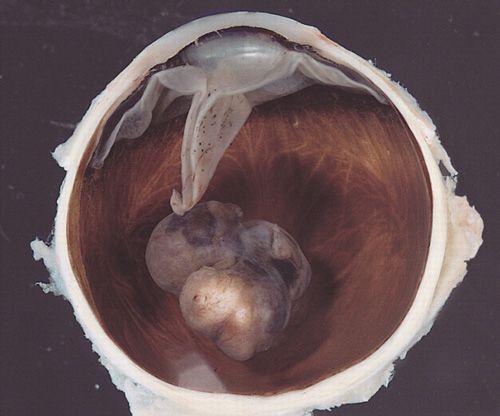
Ipilimumab, a monoclonal antibody against cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4 (CTLA-4), given alone or in combination with vaccine,w increased overall survival (OS) in patients with unresectable stage III/IV melanoma for whom previous treatment had failed, according to phase III trial results presented at the 44th annual meeting of ASCO (abstract 4). The double-blind randomized study evaluated ipilimumab and vaccine therapy with gp100 alone and in combination. Patients were assigned to receive ipilimumab (n = 137), ipilimumab and gp100 (n = 403), or gp100 alone (n = 136). Ipilimumab at a dosage of 3 mg/kg was given once every 3 weeks for four cycles, and gp100 was given at 1 mg every 3 weeks for four cycles. The primary endpoint was overall survival (OS). After 12 months, 46% of patients receiving ipilimumab alone, 44% receiving ipilimumab plus gp100, and 25% receiving gp100 were still alive. The hazard ratio (HR) for OS demonstrated a 32%–34% reduction in the risk for death in the two ipilimumab arms vs the gp100 arm alone (P = .0026 for ipilimumab alone vs gp100; P = .0004 for the combination vs gp100).