A prospective phase 2 trial evaluated the use of de-escalation therapy for patients with p16-positive squamous cell carcinoma.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


A prospective phase 2 trial evaluated the use of de-escalation therapy for patients with p16-positive squamous cell carcinoma.
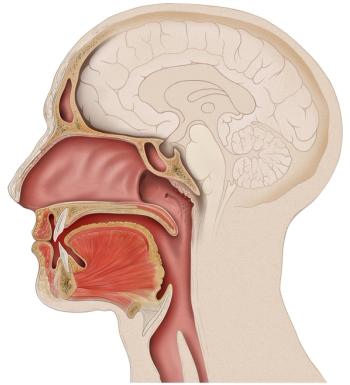
The role of multimodal approaches such as FDG-PET imaging may require further investigation in patients with human papillomavirus–positive oropharyngeal cancer, according to Samuel Regan, MD.
The use of postoperative adjuvant radiation therapy led to less weight loss in patients with HPV-positive oropharynx cancer, according to Wade L. Thorstad, MD.
Frontline pembrolizumab with or without chemotherapy appears to remain a standard of care for patients with recurrent or metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma based on data from the LEAP-010 study.

Results from a phase 1/2 trial show clinical activity of APG-115 in patients with p53 wild-type salivary gland cancer.
Results from cohort A of a pilot study of patients with HPV–associated oropharyngeal carcinoma did not meet its primary end point.

Those with breast cancer who have undergone implant-based reconstruction following mastectomy have similar outcomes with hypofractionated vs conventionally fractionated radiotherapy.

Diagnostic CT-enabled radiation therapy also reduces patient-reported time burden in the palliative setting.
Data from the FABREC trial support the use of hypofractionated postmastectomy radiotherapy in patients with breast cancer following implant-based reconstruction.

From shortening treatment duration without compromising efficacy in breast and prostate cancer to improving quality of life, experts share the main takeaways from the 2022 ASTRO Annual Meeting.

PSMA-targeting PET ligand 18F-rhPSMA-7.3 yielded high detection rates for patients with recurrent prostate cancer regardless of factors such as PSA levels, PSA doubling time, or Gleason scores, according to Benjamin H. Lowenritt, MD, FACS.

Pooling data with other radiation trials, looking more closely at central non-small cell lung cancer, and exploring secondary outcomes represent the next steps in terms of analyzing stereotactic body radiation (SBRT) vs conventional hypofractionated radiotherapy (CRT), according to Anand Swaminath, MD.

Findings from the phase 3 CALLA trial indicated that intensity modulated radiation therapy was administered in 88.1% of patients with high-risk locally advanced cervical cancer treated with durvalumab and chemoradiotherapy vs 88.1% with placebo and chemoradiotherapy.

Anand Swaminath, MD, reviews the design of the phase 3 LUSTRE trial comparing a 3-week conventional radiotherapy regimen with stereotactic body radiotherapy among patients with stage I medically inoperable non-small cell lung cancer.

Future focuses following the phase 3 SPOTLIGHT trial will include identifying sites of recurrence and different intensity levels for 18F-rhPSMA-7.3 in suspected recurrent prostate cancer, according to Benjamin H. Lowenritt, MD, FACS.

Stereotactic body radiation therapy yielded numerical improvements in terms of local control compared with conventional hypofractionated radiotherapy among patients with stage I medically inoperable non–small cell lung cancer, according to findings from the phase 3 LUSTRE trial.

Jyoti S. Mayadev, MD, indicated that durvalumab (Imfinzi) plus chemotherapy resulted in low rates of high-grade late-onset toxicities in the phase 3 CALLA trial, which may be due in part to the quality of the technology employed during the study.

The goal of the analysis of the phase 3 SPOTLIGHT trial was to evaluate how clinical factors impact 18F-rhPSMA-7.3 detection rates in a population of patients with suspected recurrent prostate cancer, according to Benjamin H. Lowenritt, MD, FACS.

Data from the phase 3 LUSTRE trial indicated that stereotactic body radiotherapy is a safe and effective alternative to conventional radiation for use in patients with stage I medically-inoperable non-small lung cancer, according to an expert from Juravinski Cancer Centre in Canada.

Jyoti S. Mayadev, MD, indicated that future research for cervical cancer will be focused on combination immune checkpoint inhibitors and biomarker research.

Novel PSMA-targeting PET ligand 18F-rhPSMA-7.3 adds to the recurrent prostate cancer armamentarium, according to Benjamin H. Lowentritt, MD, FACS.

Durvalumab appeared to have no impact on the ability to deliver safe and timely radiation therapy to patients with high-risk locally advanced cervical cancer, according to Jyoti S. Mayadev, MD.
Supplemental radiation doses delivered concomitantly with hypofractionated whole breast irradiation in 15 fractions demonstrated non-inferior ipsilateral breast recurrence and similar toxicity compared with sequential boosts following whole breast irradiation in high-risk early-stage breast cancer.
The addition of metastasis-directed therapy to intermittent hormone therapy appeared to improve survival in patients with oligometastatic prostate cancer, according to early data from the phase 2 EXTEND trial.
Patients with prostate cancer who experienced an increase in prostate-specific antigen level after radical prostatectomy appeared to benefit from a short course of androgen deprivation therapy after post-operative immediate salvage radiotherapy.
Induction chemotherapy combined with concurrent lobaplatin chemoradiotherapy improved safety outcomes without sacrificing efficacy vs a cisplatin-based regimen in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.

The 12-month progression-free survival rates among patients with high-risk locally advanced cervical cancer were comparable with durvalumab plus chemoradiotherapy vs placebo plus radiotherapy.
Data from the phase 3 SPOTLIGHT trial indicated that 18F-rhPSMA-7.3 PET yielded a positive detection rate in patients with recurrent prostate cancer, and increased along with prostate-specific antigen level.
Data from the phase 3 CALLA trial indicated that multidisciplinary collaboration and a good quality control strategy are key to providing optimal chemoradiotherapy delivery in locally advanced cervical cancer.
Results from the phase 2 NRG-HN004 trial found durvalumab plus radiotherapy did not show improved progression-free survival vs cetuximab in patients with locoregionally advanced head and neck cancer who had a contraindication to cisplatin.