
Lead study author Ruben Mesa, MD, discusses findings from the MOMENTUM trial assessing the use of momelotinib in the treatment of myelofibrosis.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


Lead study author Ruben Mesa, MD, discusses findings from the MOMENTUM trial assessing the use of momelotinib in the treatment of myelofibrosis.

Chung-Han Lee, MD, PhD, and colleagues discuss the case of a patient with renal cell carcinoma, touching on optimal treatments, toxicities, and other factors.
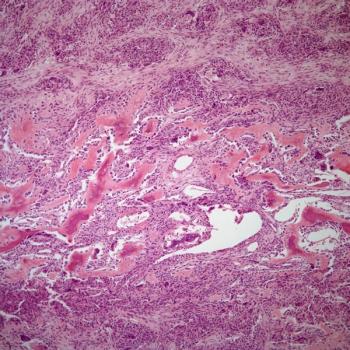
Findings from a phase 2 trial suggest that trabectedin plus radiotherapy is a tolerable treatment option in patients with myxoid liposarcoma despite yielding an unsatisfactory overall response rate.

C. Ola Landgren, MD, recaps a recent panel discussion of the rapidly changing treatment landscape in multiple myeloma, and prospects for future development.

A panel of experts discuss the updated results of the phase 3 CLEAR trial presented at the 2022 International Kidney Cancer Symposium.
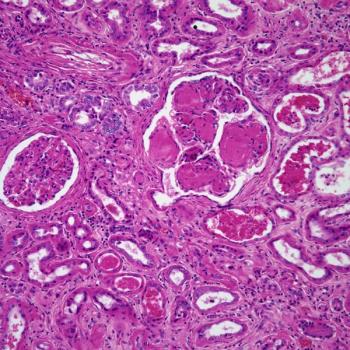
Findings from the phase 1/2 MajesTEC-1 trial suggest that preemptively planning and promptly managing cytokine release syndrome with supportive care in patients with multiple myeloma treated with T-cell–engaging bispecific antibodies may be beneficial.

Preet M. Chaudhary, MD, and his medical team discuss graft-vs-host disease (GVHD) and their treatment experiences alongside a patient, Hector Cuevas.
An additional 5 years of adjuvant aromatase inhibition following initial therapy may improve survival outcomes among disease-free patients with postmenopausal breast cancer, according to results from the phase 3 AERAS study.

Although findings from a population-based meta-analysis suggest a greater risk of death in patients due to cancers diagnosed during pregnancy and postpartum, not all disease sites had the same risk.
The FDA requests additional data and a safety update regarding N-803 plus BCG as a treatment for patients with BCG-unresponsive non-muscle invasive bladder carcinoma.
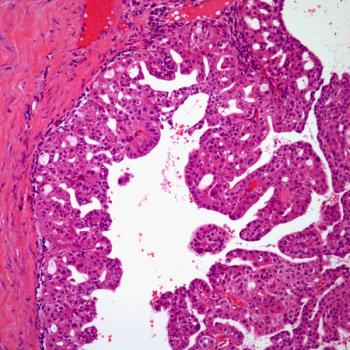
PYX-201 is currently being investigated in a phase 1 trial in patients with solid tumors.
The next leap forward in breast cancer is identifying patients who would best benefit from a treatment de-escalation approach through the use of precision medicine.

Co-editor-in-Chief Howard S. Hochster, MD, discusses persistent obstacles to the effective use of biosimilars in clinical practice.

“Sometimes we have to advocate, but mostly we have to hire experts in our practice who can access these agents through free assistance programs, partial assistance, copay assistance, etc. That is an effort, a big part of the infrastructure and practices, to be able to access therapies.”
Findings from a nested case-control study may enable individualized colorectal cancer risk estimations for Hodgkin lymphoma survivors who receive radiotherapy plus procarbazine.
China’s National Medical Products Administration has also approved zanubrutinib as a treatment for patients with Waldenström macroglobulinemia based on findings from the phase 3 ASPEN trial.

A post hoc analysis of the phase 3 TITAN trial highlights an association between PSA decline and survival among patients with metastatic castration-sensitive prostate cancer who were treated with apalutamide plus androgen deprivation therapy.
Findings from the phase 3 ORIENT-31 trial support the use of sintilimab plus chemotherapy as a potential novel treatment strategy for those with EGFR-mutated nonsquamous non–small cell lung cancer.
The CAR T-cell product has a neoantigen-specific T-cell receptor that is located and classified via a T-cell receptor discovery platform.

Investigators of a phase 1/2 trial report that CAR T cells targeting disialoganglioside GD2 may result in long-lasting antitumor activity in young patients with high-risk neuroblastoma.
Treatment with socazolimab plus carboplatin and etoposide appears safe in patients with small cell lung cancer, according to preliminary phase 1 study findings.
Findings from a recent phase 1b study suggest that magrolimab plus azacitidine may be an “important addition” to the higher-risk myelodysplastic syndrome treatment landscape.
Data from the phase 3 ZIRCON trial evaluating 89Zr-DFO-girentuximab in patients with renal tumors may be practice changing, according to an expert from the University of California Los Angeles.
Investigators will assess INB-400 as a treatment for patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma in a phase 2 trial expected to initiate in the second half of 2023.

Rakhshanda Rahman, MD, FRCS, FACS, emphasizes the importance of educating patients and physicians on the potential risks and benefits of new approaches and technologies involved in the de-escalation of breast cancer treatment.
Treatment with isolated hepatic perfusion appears to yield improved progression-free survival compared with best alternative care in patients with isolated uveal melanoma liver metastases.
An ancillary analysis of 2 clinical trials finds that pathologic complete response may be a prognostic factor of clinical outcomes in soft tissue sarcoma in future studies.

A recovery tracker and other digital tools may be useful in helping to manage patient symptoms following debulking surgery for gynecologic cancer, according to an expert from Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center.
The addition of pembrolizumab to conventional chemotherapy appears tolerable and effective in a cohort of patients with relapsed/refractory classic Hodgkin lymphoma, according to data from a phase 2 trial.

According to an expert from University Hospitals, integrative oncology has a place in the treatment of patients with kidney cancer alongside palliative care, psycho-oncology, and physical therapy.