Tumor shrinkage is a valid indicator of response to VEGF inhibition among patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma when evaluated by a single radiologist observer.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


Tumor shrinkage is a valid indicator of response to VEGF inhibition among patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma when evaluated by a single radiologist observer.

The second generation VEGFR inhibitor axitinib did not significantly improve progression-free survival in first-line treatment of patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma compared with patients treated with sorafenib.
Image-guided radiofrequency ablation may be an effective alternative treatment for small renal cell carcinoma tumors, according to the results of a recent study.
Results of a recent study indicate that patient progression-free survival at 3 months and 6 months was predictive of the overall survival among metastatic RCC patients treated with interferon alpha and bevacizumab.

The mTOR inhibitor everolimus showed clinical efficacy for the initial treatment of advanced papillary renal cell carcinoma, according to the phase II results of the RAPTOR trial.

The results of the study comparing Aveo’s tivozanib to sorafenib for the treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma showed no improvement in overall survival, the basis for the FDA’s rejection of the company’s new drug application earlier this year.
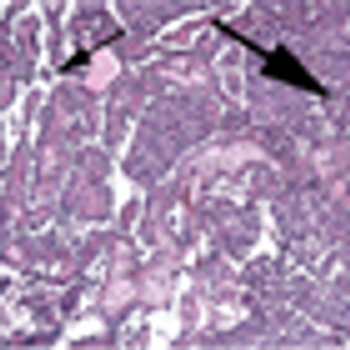
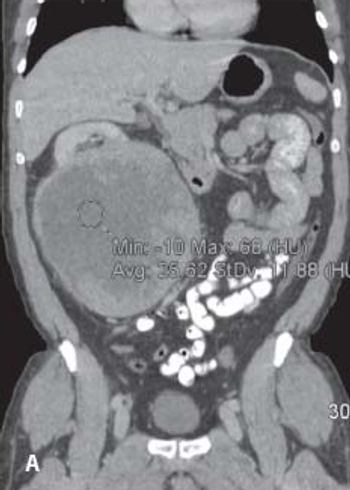
The patient is a 66-year-old male who presented to his primary care physician with a 3-week history of painless gross hematuria. He underwent a renal ultrasound that showed a left kidney mass.

A head-to-head comparison of pazopanib and sunitinib for the treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma showed that the two drugs resulted in similar progression-free survival, but also indicated that pazopanib may have a favorable safety profile.

Surgeons saw advantages in robotic, over laparoscopic, ultrasound probes during robotic partial nephrectomy, and similar perioperative outcomes and margin rates.

Undergoing nephron-sparing surgery for small renal masses substantially reduced the risk of moderate renal dysfunction compared with radical nephrectomy, but not that of kidney failure among patients enrolled in the EORTC 30904 trial.
General practitioners took longer to suspect a diagnosis of bladder or renal cancer in women compared with men, according to a recent study.
A high skeletal muscle density has been linked to a twofold prolonged survival in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma compared with patients with low muscle density, according to a new study.

There has never been a referendum on IL-2. True, in the era of paradigm-shifting therapies, IL-2 may be overlooked at times, but it must not be excluded from the conversation.

Ultimately, as agents in both VEGF-targeted and immunotherapy classes with lower toxicity rates are developed, questions of combination and sequence will inspire clinical investigations of strategies that, it is hoped, will maximize both the quantity and quality of life for patients with RCC. Melanoma therapy drug development continues to lead the way with regard to what is therapeutically possible with immunotherapy-and suggests that HD IL-2 continues to be relevant in today’s treatment landscape.
In this review, we examine the currently approved options available for these disease processes, including the newer agents and selected combinatorial approaches under investigation, and we attempt to identify the role of high-dose IL-2 in the context of current clinical practice.
Bone metastases result in poorer outcomes for those patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC), who were treated with a molecularly targeted therapy. The results were presented in two separate analyses at the annual ASCO meeting.
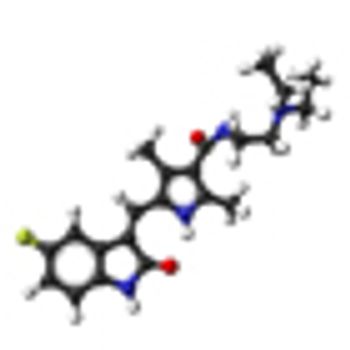
The mTOR inhibitor everolimus failed to prove progression-free survival noninferiority compared with the VEGF-targeting tyrosine kinase inhibitor sunitinib when given as first-line treatment in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma.
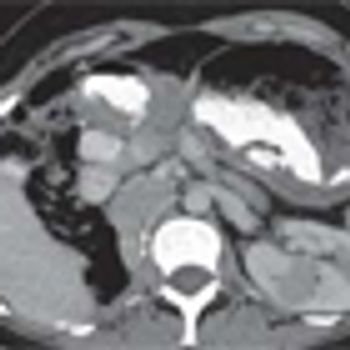
Researchers observed durable responses in patients with renal cell carcinoma treated with the PD-L1 antibody MPDL3280A. The study, which was presented at the 2013 ASCO Annual Meeting, was one of the few immune therapy trials that allowed patients with non-clear cell histologies and some clinical activity was observed in these patients.
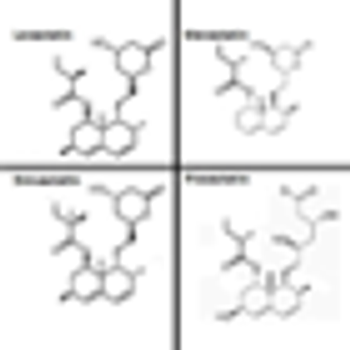
The use of statins was independently associated with improvements in overall survival and disease-specific survival among a group of patients who had undergone partial or radical nephrectomy for renal cell carcinoma.
A study found that robotic partial nephrectomy to remove kidney cancer tumors resulted in better outcomes, but also had significantly higher hospital charges. The data were presented at the annual meeting of the American Urological Association.

The FDA’s Oncologic Drugs Advisory Committee has voted 13 to 1 against AVEO's drug tivozanib for the treatment of patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma.

A new immunoassay that tests for the presence of nicotinamide N-methyltransferase (NNMT), L-plastin (LCP1), and nonmetastatic cells 1 protein (NM23A) may be an effective method for the early detection of malignant kidney cancer.
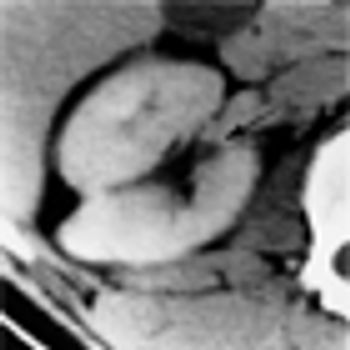
Even those renal cell carcinomas (RCCs) that are smaller than 4 cm may put patients at risk for aggressive cancer, according to a new study presented at the 28th Annual European Association of Urology Congress in Milan, Italy.

Acetaminophen and nonaspirin nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs were associated with a 28% increased risk of developing kidney cancer, according to the results of a recently published meta-analysis.

High levels of physical activity were linked with a 22% decreased risk for renal cancer, according to a meta-analysis that looked at results from 19 studies that quantified the relationship with physical activity and renal cancer.