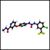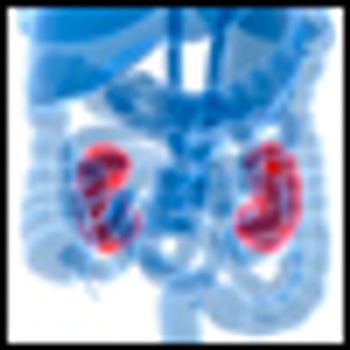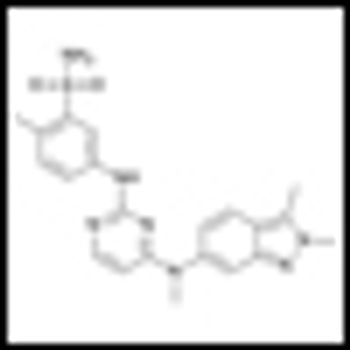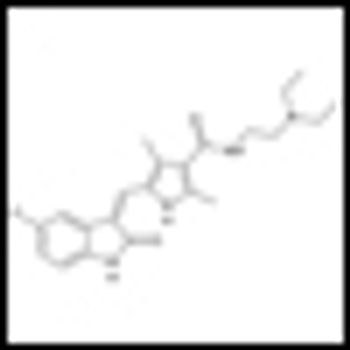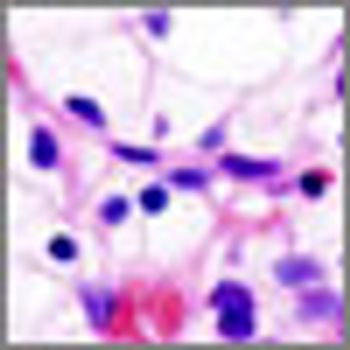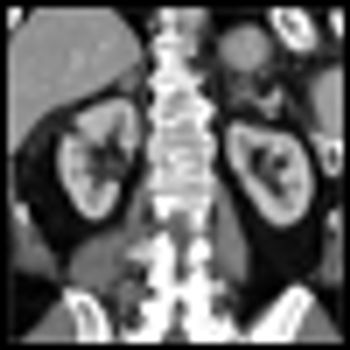
The mTOR inhibitor everolimus (Afinitor) has been found to significantly reduce the size of angiomyolipomas, the slow-growing benign tumors commonly associated with tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC) and sporadic lymphangioleiomyomatosis, according to the results of the phase III EXIST-2 study.