
New immunotherapies that target PD-1 are now showing promise for first-line and second-line treatment of metastatic bladder cancer.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


New immunotherapies that target PD-1 are now showing promise for first-line and second-line treatment of metastatic bladder cancer.

Pembrolizumab showed clinical activity against some cases of enzalutamide-refractory metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer.

Treatment with cabozantinib resulted in significantly improved PFS and overall response vs sunitinib for patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma.

Patients with renal cell carcinoma at high risk for recurrence had prolonged disease-free survival when treated with sunitinib compared with placebo.

Patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) and visceral metastases (liver and lung) fare better with the androgen receptor inhibitor enzalutamide than placebo, according to a new analysis from the phase III AFFIRM trial.

Combining two cancer immunotherapies to target both the interleukin 10 (IL-10) and programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) receptors has yielded promising early results for some patients with renal cell carcinoma and non-small cell lung cancer.

The FDA announced a modification to the recommended dosage regimen for nivolumab (Opdivo) for renal cell carcinoma (RCC), metastatic melanoma, and non–small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC).

Men who have vasectomies do not have a higher risk of prostate cancer and are not more likely to die from the disease, according to a large, prospective study.

The gene known as β-Klotho (KLβ) appears to play an important role in tumor invasion and progression in patients with bladder cancer, and urine KLβ levels may act as a useful biomarker, according to a new study.

Investigators at the University of Colorado Cancer Center and Yale University are now reporting in the journal Cancer Cell on a new understanding of the cancer suppressing gene RhoDGI2 and how it may be involved in metastatic bladder cancer.

Patients with metastatic RCC and a BMI of 25 or greater had significantly longer overall survival compared with patients with a BMI of less than 25, according to the results of a recent study.

While survival at 10 years was nearly identical (close to 99%), a new study found that localized prostate cancer is more likely to metastasize in men receiving active surveillance compared with those who have surgery or radiation therapy.
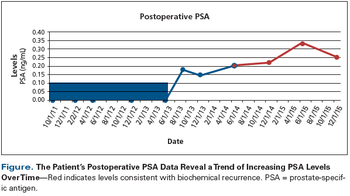
A 66-year-old Caucasian man with a history of hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and rheumatoid arthritis was diagnosed with prostate cancer.

The combination of bevacizumab and everolimus had efficacy in patients with unclassified non–clear cell renal cell carcinoma characterized by papillary features, resulting in an objective response rate of 43%.

Patients with non-urothelial bladder cancer are more commonly upstaged during surgery compared with urothelial cancers.

A new class of agents known as hypoxia-inducible factors-2 inhibitors may be more effective and better tolerated than sunitinib (Sutent), the current standard of care, in patients with renal cell carcinoma.
Investigators think they may have found a strong predictor of which men with prostate cancer will develop resistance to androgen deprivation therapy.

PSA failure in men with localized, intermediate- or high-risk prostate cancer was associated with increased all-cause mortality in only those patients with no or minimal comorbidity.

Patients with RCC who underwent simultaneous nephrectomy and hepatic resection had similar postoperative mortality, long-term survival, and cancer-specific survival as those patients who underwent metastasectomy or en bloc resection of neighboring non-hepatic organs.
A model based on a series of PSA tests can predict the time to relapse in prostate cancer patients who underwent radical prostatectomy, according to a new study.

Despite treatment advances for renal cell carcinoma, biomarkers are urgently needed for earlier diagnosis and treatment, and quicker assessment of treatment efficacy. Development of such tools has lagged behind biomarker research for more common cancers, and despite encouraging findings from several newly published preclinical studies.

Although the overall incidence of programmed cell death 1 (PD-1) inhibitor-related pneumonitis is rare, the serious adverse event may occur more commonly in certain solid tumor types like non–small-cell lung cancer and renal cell carcinoma.

The incidence of early-stage prostate cancer in men 50 years and older continued a decline reported earlier, with lower rates in 2013 compared to 2012. This is a likely result of the October 2011 recommendation from the USPSTF against routine PSA testing in all men.

Patients with kidney cancer who are considered to be in poor functional health were less likely to receive cancer-directed surgery to treat their disease.

Noncoding RNA appears to be involved in the epigenetic regulation of prostate cancer, according to findings published in Nature Genetics.