
Undergoing complete metastasectomy for metastatic renal cell carcinoma was associated with improved survival outcomes, according to the results of a meta-analysis.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


Undergoing complete metastasectomy for metastatic renal cell carcinoma was associated with improved survival outcomes, according to the results of a meta-analysis.

A novel urine-based DNA test was effective at detecting bladder cancer, and in particular at identifying patients with gross hematuria who do not require cystoscopy.

Certain patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma safely underwent active surveillance of their disease prior to undergoing systemic therapy.

Outcomes after salvage radiotherapy are affected by variables related to prostatectomy for men with prostate cancer, but its use at lower PSA levels may improve outcomes.

Patients with RCC had greater postsurgical decreases in kidney function compared with patients with upper tract urothelial carcinoma.

New NCCN guidelines regarding genomic profiling will likely yield important opportunities to improve the care of patients with advanced bladder cancer.

A new study has found a series of potential microRNA biomarkers that could predict tyrosine kinase inhibitor response in RCC patients.

In this paper, we review the use of serum tumor markers in risk assignment and response evaluation; the treatment of previously untreated and relapsing patients; the role of surgical resection of residual disease, including retroperitoneal node dissection; and the importance of clinical trials for addressing unanswered questions and testing new therapies.

Metastatic prostate cancer is more strongly associated than localized disease with germline mutations in DNA repair genes like BRCA1 and BRCA2.

Canadian researchers have tentatively identified urine protein signatures that appear to differentiate aggressive from low-risk prostate tumors.

Both African-American and Caucasian patients with advanced RCC have seen improved survival with targeted therapies, though African-Americans still experience survival disadvantages.

A randomized phase III trial found that a hypofractionated radiotherapy regimen was not superior to, but generally equivalent to a conventional radiotherapy scheme in men with localized prostate cancer.

Compared to everolimus, the oral tyrosine kinase inhibitor cabozantinib improves objective tumor response, delays disease progression, and prolongs overall survival time among patients with RCC.

A database analysis showed that the addition of external beam radiotherapy to ADT significantly improves overall survival in men with metastatic prostate cancer.

Higher than average PSA levels in middle age may be predictive of a higher risk of lethal prostate cancer later in life.

Long-term follow-up of a phase I and a phase II study shows that nivolumab produces strong overall survival benefit in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma.

Patients with metastatic RCC who undergo cytoreductive nephrectomy plus targeted therapy have better survival over those treated only with targeted therapy.

Cabozantinib significantly improved the overall survival of patients with previously treated advanced RCC, according to the second interim analysis of the METEOR trial.

In this peer-to-peer discussion Dr. Grivas and Dr. Palmbos examine the role of neoadjuvant chemotherapy in bladder cancer and weigh the various trial data guiding these treatment decisions.
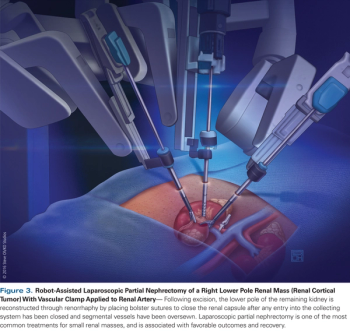
In this review, we summarize the diagnosis of small renal masses, the role of renal mass biopsy, different treatment strategies, and future directions, including emerging molecular biomarkers.

More research is needed to define the optimal radiotherapy and chemotherapy regimen for male urethral carcinoma. However, modern chemoradiation is a feasible treatment option for motivated men with urethral carcinoma who want to preserve their organs.

This article will review select novel targets and approaches relevant to urothelial cancer.

Since the development of first-line cisplatin-based combination chemotherapy with methotrexate, vinblastine, doxorubicin, and cisplatin almost 3 decades ago, there have not been major advances in the treatment of this disease.

Patients with T1 bladder cancer on re-resection achieve the best possible survival benefit by IRC and thorough pelvic lymph node dissection.

Nivolumab is safe and effective in patients with metastatic bladder cancer refractory to prior lines of platinum-based chemotherapy, according to findings from the open-label, phase I/II CheckMate 032 trial.