
The FDA has granted breakthrough therapy designation to a novel treatment known as CTL019, a therapy intended for patients with relapsed/refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL).

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


The FDA has granted breakthrough therapy designation to a novel treatment known as CTL019, a therapy intended for patients with relapsed/refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL).

Is PCNSL resection safe? Evidence from clinical trials in which enrollment follows surgery-such as G-PCNSL-SG-1-is not valid proof of the safety of resection.
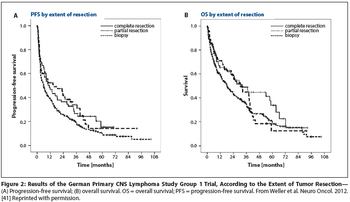
Relatively few patients with primary diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (PCNSL) will have tumors that are amenable to resection. In the absence of the highest quality data, at least it is good to know that in the modern era, patients with PCNSL are probably not harmed by judicious tumor resection.

For the practicing medical or neuro-oncologist, the treatment approach would currently not change, given that systemic therapy should be started as soon as the diagnosis of PCNSL is made and the patient is stable from a neurosurgical perspective. In most cases, one would not refer the patient back to the surgeon for additional debulking.

Prophylaxis with tacrolimus/sirolimus provided equivalent graft-vs-host disease-free survival in patients undergoing matched, related donor hematopoietic cell transplantation.

Lymphocyte infusions are extremely effective therapy in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia who relapse after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, and the timing of the infusion is relatively unimportant, according to a new study.

Researchers from Japan believe they have identified a novel staging system based on hemoglobin and plasmacytoma that may help to stratify patients with multiple myeloma who are treated with novel therapeutics.
Carfilzomib given at a higher dose as a slow intravenous infusion over 30 minutes resulted in a very high response rate in a heavily pretreated myeloma population.
Long-term outcomes of patients treated for pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) with modern treatment protocols are good, with an overall low risk for serious long-term side effects.

The FDA has approved the drug belinostat to treat patients with relapsed or refractory peripheral T-cell lymphoma.

Measuring changes in levels of BCR-ABL in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) can help predict treatment outcomes and disease progression, according to a new study.
Researchers have identified Down syndrome as a risk factor for infection-related mortality among pediatric patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia.


A comparison of melphalan, prednisone plus either thalidomide or lenalidomide found that patients assigned to lenalidomide had fewer grade 3 or higher toxicities and a better quality of life at the end of induction therapy.

This review will focus on newer FDA-approved targeted therapies associated with type II chemotherapy-related cardiac dysfunction, or generally reversible cardiotoxicity, and will provide the latest information on the incidence and clinical spectrum of cardiotoxicity associated with each therapy, modifiable risk factors where known, and the mechanisms of cardiotoxicity.
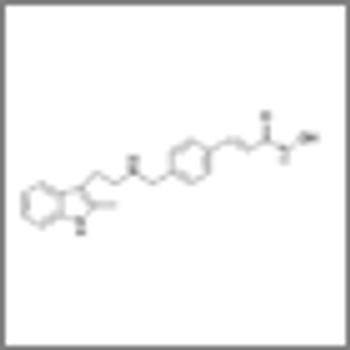
Treatment of relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma with the three-drug combination of panobinostat/bortezomib/dexamethasone resulted in a nearly 4-month improvement in progression-free survival compared to treatment with bortezomib/dexamethasone alone.
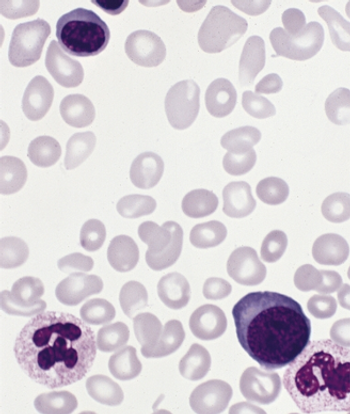
Ruxolitinib was significantly better than the best available therapy in a phase III, open-label trial of patients with polycythemia vera who were resistant to or intolerant of hydroxyurea.
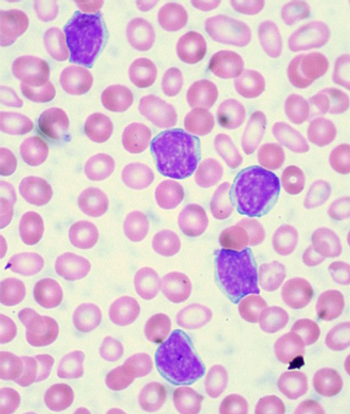
A phase II trial of the selective spleen tyrosine kinase (Syk) inhibitor GS-9973 showed substantial biologic activity in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL).
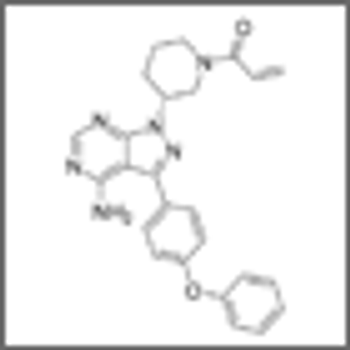
Ibrutinib substantially increased progression-free survival and overall survival over ofatumumab in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL), according to the results of the RESONATE trial.
Treatment with lenalidomide and dexamethasone improved quality-of-life measures in multiple myeloma patients, according to a study presented at the 2014 ASCO Annual Meeting.
Continuous therapy produces drastically better progression-free survival and overall survival outcomes in patients with multiple myeloma. A novel endpoint involving time to second progression is an important tool in evaluating this type of treatment in the future.

As part of our coverage of the 2014 American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting, we discuss the pros and cons of follow-up imaging in lymphoma.

The new drug volasertib, which is in trials for the treatment of patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML), has been granted orphan drug designation by the FDA.

Obesity or underweight status at diagnosis can influence outcomes in pediatric ALL patients, but a new study shows that the risk can be mitigated if weight status changes following treatment induction.

A novel agent known as BL-8040 will enter phase I/II testing for the treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia, according to BioLineRx, the company developing the drug.