
Our heads hit the pillow later at night as the complexity of treating DLBCL increases, but we are well rested on account of the progress that is being made.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


Our heads hit the pillow later at night as the complexity of treating DLBCL increases, but we are well rested on account of the progress that is being made.

Rationally designed clinical trials investigating novel agents in patient populations enriched for those who are most likely to benefit will be instrumental for expediting progress. With respect to DLBCL, it has become clear that one treatment no longer fits all.

With the progress in diagnostic methods that has made it possible to decipher the genetic code of DLBCL within a relatively short time, and with the increasing number of drugs that are entering clinical trials, our next big challenge is to enroll patients in trials in a timely manner.
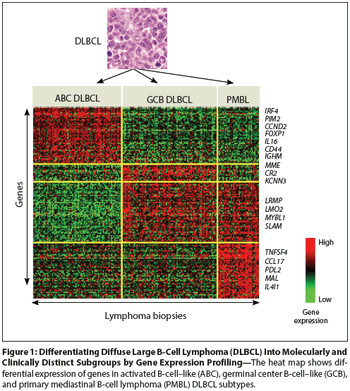
The classification of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma into three distinct molecular diseases--germinal center B-cell–like subtype, an activated B-cell–like subtype, and a primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma subtype--has laid the foundation for the development of new agents and novel strategies that target individual subtypes.

The novel experimental drug sotatercept increased bone mineral density and bone formation in patients with osteolytic lesions of multiple myeloma who had not used bisphosphonates, a phase II study showed.
New trial results show that a novel, oral metabolic inhibitor has demonstrated early activity in relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia (AML), according to data presented at the annual meeting of the American Association of Cancer Research.

Results of a new study indicate that half of patients with multiple myeloma were referred to specialist palliative care.

A new study of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) suggests that event-free status at 2 years post-treatment is a useful endpoint both for research and for patient counseling.
A subgroup of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) cells that were “sticky,” or adherent to plastic, showed higher expression levels of BCR-ABL and were more resistant to treatment with the tyrosine kinase inhibitor imatinib.
A phase II trial of mogamulizumab showed that the agent has meaningful antitumor activity in patients with relapsed peripheral T-cell lymphoma and cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, and acceptable toxicity.

MolecularMD and Novartis are working on a diagnostic test to help determine which chronic myeloid leukemia patients may be candidates to stop taking nilotinib.

Although the cure rate remains high in women who present with bulky mediastinal stage I–II HL, the challenge remains to balance efficacy and minimize long-term toxicities.

The combination of bortezomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone resulted in a partial response or better in more than 60% of patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma, according to results of a phase II trial.

Results of a large meta-analysis indicated that treatment with lenalidomide for newly diagnosed multiple myeloma was associated with an increased risk for developing secondary hematologic malignancies.

Contrary to some previous research as well as popular belief, living underneath or near to power lines as a child may not have any notable effect on childhood leukemia risk, according to a new case-control study conducted in the United Kingdom.

Researchers have identified distinct pre-leukemic hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) patients.
A score based on an epigenetic signature of hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) is highly prognostic for patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML), according to a new study.

The FDA has approved ibrutinib (Imbruvica) as a single-agent treatment for previously treated patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), under the FDA’s accelerated approval program.
Results from a phase I/II trial indicate that carfilzomib may be a safe and effective substitute for bortezomib in multiple myeloma patients whose disease progressed during treatment with a bortezomib-containing regimen.

More than one-third of African American patients with monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance or multiple myeloma were found to have an inherited risk factor for the disease, according to the results of a European study.
The combination of idelalisib with rituximab improved survival in relapsed CLL, and idelalisib also showed antitumor activity as a single agent in patients with indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
Activating mutations in the beta-catenin gene in bone cells is shown to contribute to the development of acute myeloid leukemia.

After significant improvement in progression-free survival with ibrutinib over ofatumumab, an independent data monitoring board has recommended stopping a phase III trial involving patients with relapsed or refractory CLL or SLL.
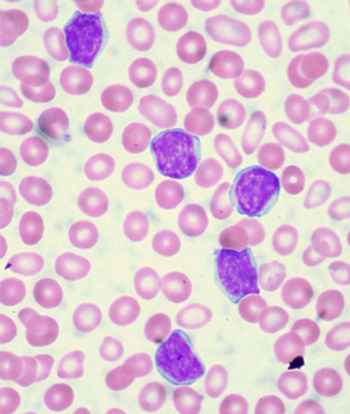
In a new study, combining the anti-CD20 antibody obinutuzumab with chlorambucil improved outcomes over rituximab and the same agent in chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients with coexisting conditions.

Most physicians are less aware of clinical presentations of the various heavy chain diseases, due in great part to their low incidence and highly variable clinical course. Heavy chain diseases are rare lymphoproliferative B-cell disorders whose hallmark is the accumulation and secretion of truncated constant heavy chains without the associated light chains.