
How often do we choose the “second best” treatment as initial therapy for our patients with cancer? The management of chronic myeloid leukemia should be no different.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


How often do we choose the “second best” treatment as initial therapy for our patients with cancer? The management of chronic myeloid leukemia should be no different.

I am very comfortable in using imatinib as initial therapy in most patients who present in chronic phase, with the possible exception of patients with more advanced disease and higher Sokal scores.

The present guidelines review epidemiology, pathology, presentation, workup, staging, prognostic factors, and treatment options for patients with localized nodal indolent lymphoma, with an emphasis on radiation guidelines, including radiation dose, field design, and radiation techniques.

A study from the Mayo Clinic/University of Iowa assessing the use of surveillance CT scans to detect DLBCL relapses found that the majority of relapses occurred outside of regularly scheduled visits and concluded that it is important to educate patients to be more alert to signs and symptoms of relapse.

Dr. Brian Link discusses challenges in managing very elderly patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and looks ahead to future management of DLBCL in general.

Dr. Brian Link discusses clinical implications of the large Mayo Clinic/ University of Iowa study (ASCO abstract 8504) showing patient symptoms rather than scheduled surveillance imaging drove detection of relapses in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).

In this interview, we discuss the current state of therapies available in treating CML patients and the role of newer agents.

The phase II portion of the GAUGUIN study found promising activity with the anti-CD20 antibody obinutuzumab in patients with relapsed or refractory indolent NHL.

A phase I/II study found that radioimmunotherapy with 177Lu and the anti-CD20 antibody rituximab along with the chelator DOTA is safe and feasible for treatment of relapsed follicular, mantle cell, or other indolent lymphomas.

Palliation is a laudable concept and an important goal in the therapy of all patients with malignant disease. Unfortunately, in the current day and age, the adjective “palliative” is being used in a derogatory manner that suggests palliation of suffering somehow lessens the importance or impact that such a therapy has upon individuals with the disease.

By inhibiting inflammatory cytokines and controlling the signs and symptoms of myelofibrosis, the patient’s body condition improves as the disease is kept under good control. Ultimately, prolonged exposure of a patient with myelofibrosis to ruxolitinib at a clinically effective dose results in prolongation of the his or her life.
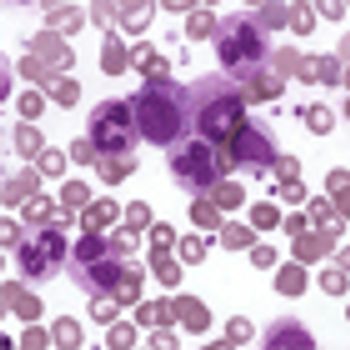
A new study validates a simple prognostic score, the EUTOS score, as a useful tool in predicting the therapeutic effects of TKIs for chronic myeloid leukemia.
ARIAD has received marketing authorization from the European Commission for ponatinib (Iclusig) in chronic myeloid leukemia and acute lymphoblastic leukemia.

In this interview we discuss acute myeloid leukemia therapy approaches and new molecular targets based on genetic analyses of the disease with a leukemia expert.
Use of the bisphosphonate pamidronate (Aredia) may be “more efficient” than standard regimens as palliative treatment for symptoms of acute symptomatic osteonecrosis in pediatric patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
Phase II trial results of the targeted agent ibrutinib in relapsed or refractory mantle-cell lymphoma show that the drug led to promising and durable responses.
Almost half of patients with chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) who discontinued imatinib treatment did not relapse, according to results of a prospective study. Those who did relapse showed continued sensitivity to imatinib when treatment started again.
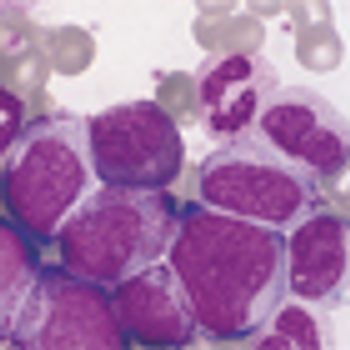
A phase II study found that an alternative imatinib treatment schedule for elderly patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) could be an effective way to reduce dosing requirements of the drug.
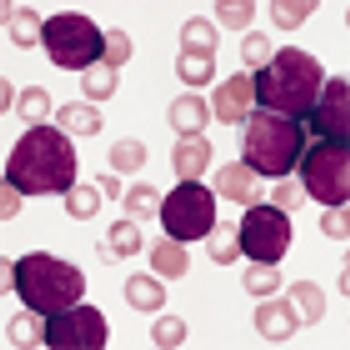
Findings suggesting that obesity substantially impairs the ability of L-asparaginase to kill leukemia cells were reported last month by investigators from The Saban Research Institute, Children’s Hospital Los Angeles.

If systemic treatment is effective enough to reliably control not only microscopic but also bulky disease, there will be little role for radiotherapy. And if systemic treatment cannot even reliably control microscopic disease, let alone macroscopic disease, there will be little role for radiotherapy, either. However, there are patients who fall into neither of these categories, and in them radiotherapy may well have a role.

DLBCL of any stage remains a systemic disease with early hematogenous spread. Thus, arguments advocating the role of IFRT do not truly address disease biology, and all future efforts to cure patients will require improved systemic therapy.
Two studies found higher rates of peripheral artery occlusive disease in nilotinib-treated chronic myeloid leukemia patients than in imatinib-treated patients.

Researchers have characterized acute myeloid leukemia, providing new genetic driver leads to help classify the disease and even stratify AML patients by risk.
Multiple myeloma patients are at increased risk of developing myelodysplastic syndrome or acute leukemia after maintenance lenalidomide or thalidomide treatment, according to a new study.
A group of experts say that cancer drug prices, especially those for chronic myeloid leukemia, have skyrocketed, making patient treatment extremely difficult.