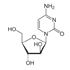
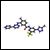
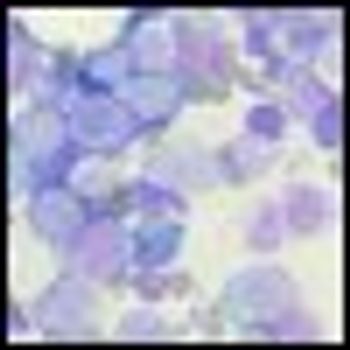
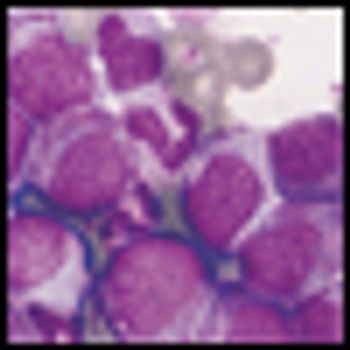
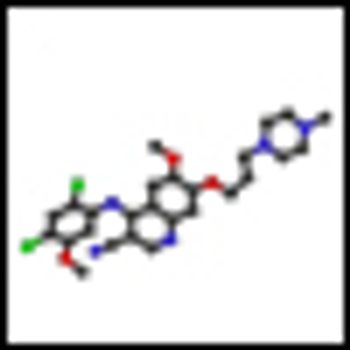
Researchers have discovered a fully human “T-cell receptor–like” monoclonal antibody specific for the Wilms tumor 1 oncoprotein-an intracellular oncogenic transcription factor that is overexpressed in a wide range of leukemias, as well as solid cancers.