In a phase I trial, DT2219, the novel bispecific ligand-directed toxin, has shown activity against relapsed and refractory B-cell lymphoma and leukemia.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


In a phase I trial, DT2219, the novel bispecific ligand-directed toxin, has shown activity against relapsed and refractory B-cell lymphoma and leukemia.
In patients with AML, post-therapy parameters including minimal residual disease and remission were found to be independent prognostic factors for outcomes.
Induction treatment for acute myeloid leukemia with amonafide L-malate/cytarabine failed to improve the rate of complete response over daunorubicin/cytarabine.
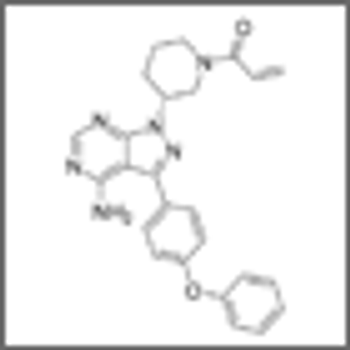
Researchers have identified patient factors linked with the discontinuation of ibrutinib therapy for reasons other than disease progression.

A new study finds that childhood cancer survivors are at risk for pituitary hormone deficiencies after radiotherapy treatment to the head.

Despite an association with improved survival, elderly DLBCL patients are less likely to receive standard-of-care chemotherapy with R-CHOP.
Researchers have shown that axitinib could be repurposed as a treatment for CML patients resistant to standard TKIs through a certain molecular mechanism.

The FDA has expanded the approved use of ibrutinib (Imbruvica) to include patients with Waldenström macroglobulinemia, a rare type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
Using genome-wide association studies, researchers have identified a germline variant that is associated with intolerance to mercaptopurine in pediatric ALL.

In a recent study of pediatric ALL, minimal residual disease was able to predict patients who were at increased risk for relapse post-allogeneic stem cell transplantation.
Socioeconomic factors are reducing the use of combined-modality treatment for early-stage Hodgkin lymphoma, despite its association with increased survival.
Long-term follow-up confirmed the previously reported result that intermittent administration of imatinib is safe and effective in CML patients.
Despite the early trial termination due to safety concerns, an analysis suggests that ponatinib offers improved efficacy over imatinib in newly diagnosed CML.

Clonal hematopoiesis with somatic mutations is strongly associated with the risk of developing blood cancers, according to a new study.
According to a report, two courses of the newly approved agent blinatumomab, for relapsed or refractory B-cell precursor ALL, will cost a staggering $178,000.
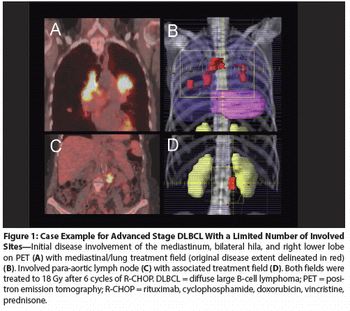
In this review, we will first briefly summarize prior attempts to improve outcomes in advanced DLBCL using systemic therapy approaches, and then we will highlight the potential role of RT in advanced DLBCL.

The major value of RT is in enhancement of local control. In localized disease, perhaps this is best achieved by using RT for patients treated with less than full-dose/course chemotherapy.

As we examine the question of which patients with DLBCL do not need RT, the first step must be to confine our review to patients who have received optimal chemotherapy.

Autologous hematopoietic cell transplantation is a safe and effective treatment option for patients with HIV-associated lymphoma, according to a study presented at ASH 2014.
Two studies presented at the 2014 ASH Meeting addressed whether an interim PET scan during and after an initial therapy can help guide treatment.
A large trial has shown that adolescents and young adults have better event-free and overall survival when treated on an intensive pediatric ALL regimen.
Early consolidation therapy with brentuximab vedotin after autologous stem cell transplant improved progression-free survival of patients with Hodgkin lymphoma.
A single cycle of blinatumomab resulted in complete minimal residual disease response in 78% of patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
An oral inhibitor of isocitrate dehydrogenase 2 (IDH2), AG-221, has shown activity and potentially durable remissions in patients with acute myeloid leukemia.

The anti–PD-1 (programmed death 1) antibody nivolumab has shown activity in patients with hematologic cancers who have failed three or more prior therapies.