Skin Cancer & Melanoma
Latest News
Latest Videos

CME Content
More News
The biologic license application for cosibelimab for patients with metastatic or locally advanced cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma is supported by findings from a phase 1 study.
“You have to be on your game continually, you have to continually self-evaluate, and the field moves quickly.”
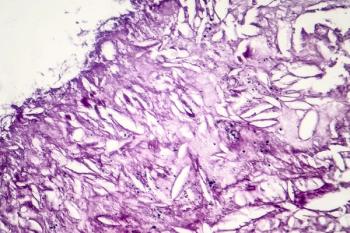
A secondary analysis from the phase 3 SWOG S1404 trial indicated that adjuvant pembrolizumab yielded improved patient-reported outcomes compared with high-dose interferon α or ipilimumab in the treatment of patients with high-risk resected melanoma.

Expert hematologist-oncologists consider the role of maintenance and consolidation following the completion of transplant in patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma.
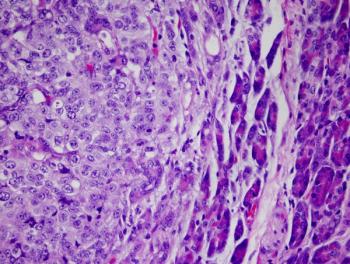
Patients with completely resected stage IIB/C melanoma experienced significant and clinically meaningful improvements in recurrence-free survival following treatment with adjuvant nivolumab compared with placebo.
Findings from the phase 3 DREAMseq trial indicated that the best course of treatment for individuals diagnosed with advanced BRAF-mutated melanoma is first-line nivolumab/ipilimumab, with BRAF/MEK inhibitors used in later-line settings.
Japan’s Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare approved pembrolizumab for use in 4 indications, including high-risk, early-stage triple-negative breast cancer, stage IIB or IIC melanoma, adjuvant renal cell carcinoma, and recurrent/metastatic cervical cancer.

Jonathan S. Zager, MD, discussed the use of percutaneous hepatic perfusion vs best alternative care for patients with hepatic-dominant ocular melanoma analyzed in the phase 3 FOCUS trial.

The European Commission based its approval of nivolumab/relatlimab for patients with a PD-L1 expression of less than 1% on the results of the phase 2/3 RELATIVITY-047 trial.
The positive results from the phase 3 CheckMate76K trial suggest that recurrence-free survival may be improved following treatment with adjuvant nivolumab vs placebo in fully resected stage IIB/C melanoma.
Patients with high-risk resectable melanoma experienced the highest event-free survival benefit when pembrolizumab was administered in the neoadjuvant settings vs the adjuvant setting
Neoadjuvant treatment with cemiplimab led to near or complete disappearance of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma in almost 64% of patients set to undergo surgery.
Results of a phase 2 trial show favorable efficacy and tolerable safety of naporafenib in combination with rineterkib, trametinib, or ribociclib in previously treated, unresectable or metastatic melanoma.
Long-term results of a phase 2 study (NCT02211131) revealed consistent efficacy at 5 years with talimogene laherparepvec in stage IIIB to IVM1a melanoma.
A randomized phase 3 trial presented at 2022 ESMO revealed better progression-free survival outcomes with tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes vs ipilimumab in stage IIIC/IV unresectable, treatment-refractory melanoma.

At ASCO 2022, Jonathan S. Zager, MD, spoke about the phase 3 FOCUS trial which analyzed patients with hepatic-dominant ocular melanoma receiving percutaneous hepatic perfusion with melphalan or best alternative care.
Patients with BRAF V600–mutated melanoma with central nervous system metastases had positive intracranial activity following treatment with atezolizumab, vemurafenib, and cobimetinib.
Nicholas Coupe, MBBS, PhD, discusses promising preliminary findings from a phase 1/2 study assessing the use of IMM60 in patients with advanced melanoma and non–small cell lung cancer.

Patients with fully resected stage IIB or IIC melanoma can now receive treatment with pembrolizumab in the adjuvant setting following its approval by the European Commission.

A sustained progression-free survival benefit was observed with nivolumab plus relatlimab-rmbw vs nivolumab alone in the phase 2/3 RELATIVITY-047 trial in treatment-naïve, unresectable or metastatic melanoma.

Distant metastasis-free and recurrence-free survival were better in patients with resected stage II melanoma who were treated with adjuvant pembrolizumab vs placebo.

By reading CT scans, machine learning could aid investigators in improving treatment decision making.

The combination of sotigalimab plus pembrolizumab was associated with a tolerable safety profile in patients with unresectable stage III or IV metastatic melanoma.

Significant Improvement in PFS Noted With Second-Line Nivolumab Plus Ipilimumab in Advanced Melanoma
Patients with advanced melanoma receiving nivolumab plus ipilimumab in the second-line setting had significant improvement in progression-free survival.
Novel BO-112 when combined with pembrolizumab may offer a new treatment option for patients with advanced melanoma and PD-1 inhibitor therapy resistance.