
Dr. Susan Domchek discusses the increased understanding of moderate penetrance genes and the importance of managing patients with these genes on a case-by-case basis.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


Dr. Susan Domchek discusses the increased understanding of moderate penetrance genes and the importance of managing patients with these genes on a case-by-case basis.

Dr. Charles Geyer discusses the phase III KATHERINE trial, which compared ado-trastuzumab emtansine vs trastuzumab in HER2-positive early breast cancer.

In this video, Dr. Allison Kurian discusses polygenic risk scores, genetic testing in diverse populations, and more as they relate to breast cancer.
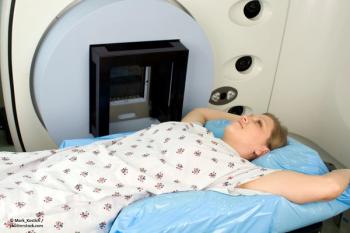
In looking to improve quality of life, researchers studied whether partial breast irradiation was just as effective as whole breast irradiation.
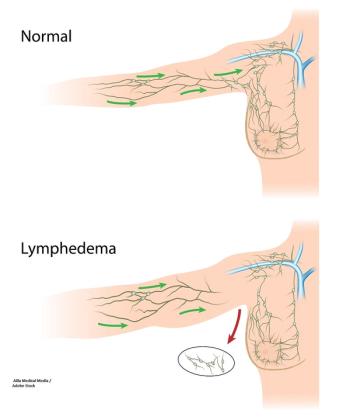
The AMAROS trial tested RT to the axillary lymph node against ALND to see if some of the morbidity associated with surgery for breast cancer could be avoided.
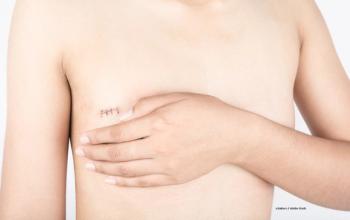
Unilateral or bilateral mastectomy can have a significant effect on quality of life when compared with breast-conserving surgery in young breast cancer survivors.
In patients with HER2-positive breast cancer treated with anthracyclines plus trastuzumab, can adding lisinopril or carvedilol reduce the risk of cardiotoxicity?

A study of a lifestyle intervention looked for improvement in disease-free or overall survival in early breast cancer patients.
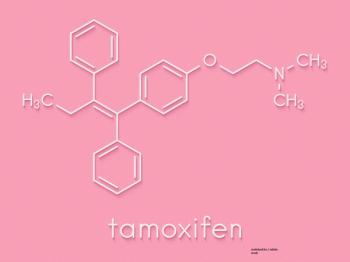
The TAM01 trial looked at whether a 5-mg/day dose of tamoxifen was effective in patients with breast intraepithelial neoplasia, or if the 20-mg/day dose was still the best option.

Undergoing axillary lymph node dissection is associated with increased arm morbidity in younger breast cancer patients compared with sentinel lymph node biopsy.

The PARP inhibitor talazoparib significantly increased progression-free survival over physician’s choice of therapy in a randomized phase III trial of patients with advanced breast cancer and a germline BRCA mutation.

This video highlights an education session from SABCS on the management of locoregional recurrence in breast cancer.

This video reviews a meta-analysis that looked at five studies testing the use of a gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) analog to protect ovarian function and preserve fertility in premenopausal women undergoing chemotherapy for early-stage breast cancer.

This video reviews controversies in the treatment of early-stage hormone receptor (HR)-positive breast cancer.

This video highlights four posters from SABCS on the use of mammography, magnetic resonance imaging, and radiomics as biomarkers for treatment response.

This video highlights four abstracts from SABCS on preserving fertility in premenopausal breast cancer patients treated with chemotherapy.

This video highlights four abstracts from SABCS investigating the use of hereditary gene panels and methods to predict prognosis in male breast cancer.

Disease-free survival after 9 weeks of adjuvant trastuzumab and standard chemotherapy was not comparable to disease-free survival after 1 year of adjuvant trastuzumab and standard chemotherapy for women with early-stage HER2-positive breast cancer.

After undergoing 5 years of adjuvant endocrine therapy, 2 years of extended anastrozole proved as effective as 5 years for preventing breast cancer recurrence among postmenopausal women with hormone receptor (HR)-positive breast cancer, according to the results of the ABCSG-16 phase III trial.

A study found that circulating tumor cells are predictive of late recurrence in patients with hormone receptor–positive, HER2-negative early breast cancer.

An antibody–drug conjugate known as sacituzumab govitecan demonstrated significant clinical activity in heavily pretreated patients with relapsed/refractory metastatic triple-negative breast cancer, according to a new study.

Treatment with gonadotropin-releasing hormone analog can safely and effectively protect ovarian function and has the potential to preserve fertility in premenopausal women undergoing chemotherapy for early-stage breast cancer.

Adding vistusertib to fulvestrant failed to demonstrate a benefit over everolimus in patients with ER-positive advanced or metastatic breast cancer.

Undergoing acupuncture significantly reduced joint pain related to treatment with aromatase inhibitors in postmenopausal women with early-stage breast cancer.

Adding trastuzumab to adjuvant chemotherapy did not result in improved rates of invasive disease-free survival in patients with early-stage breast cancer and low levels of HER2 expression, according to a new study.

Increasing chemotherapy dose intensity reduced the risk of recurrence and death over standard chemotherapy regimens, according to a meta-analysis of women with early-stage breast cancer.

The addition of the CDK4/6 inhibitor ribociclib to endocrine therapy with either tamoxifen or an aromatase inhibitor significantly improved progression-free survival among premenopausal and perimenopausal women with breast cancer.

The combination of pembrolizumab and trastuzumab showed promising clinical benefit in patients with trastuzumab-resistant HER2-positive advanced breast cancer who express PD-L1, according to a new study.

A study found no difference in outcomes between 2 and 5 years of treatment with zoledronate after chemotherapy in early breast cancer patients, suggesting the longer duration may not be necessary.

Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes have significantly higher expression of PD-L1 in pregnancy-associated breast cancer compared to nulliparous breast cancer patients. This may help predict response to therapy, among other outcomes.