
This review will examine agents with potential activity in the palliation and treatment of skeletal metastases of prostate cancer, and will weigh the clinical-outcomes evidence for and against their broad use.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!



This review will examine agents with potential activity in the palliation and treatment of skeletal metastases of prostate cancer, and will weigh the clinical-outcomes evidence for and against their broad use.

In addition to endeavors to develop new therapeutics, we should anticipate and prioritize studies that will address questions regarding the efficacy of combination therapy, timing and sequencing strategies, and the development of predictive markers to individualize and optimize therapy.

We are seeing a new era in drug development with the identification of novel intra- and extracellular targets to which therapies are being directed. Perhaps more exciting is learning how to optimize standard therapies in combination with biologic agents and radiopharmaceuticals in order to target multiple pathways in prostate cancer growth. Stay tuned!

This is a very emotional issue. Any time a group claims less screening is good, I always take it with a grain of salt-yet the data certainly seem to support that generalized screening with PSA may not impact survival in the general population.

Flax, an annual plant believed to have originated in Egypt, is cultivated around internationally and is among the world’s oldest crops.

Vitamin E supplements, rather than reducing the risk of prostate cancer have been found to increase the risk of developing the disease. The findings are a 3-year follow-up to the Selenium and Vitamin E Cancer Prevention Trial (SELECT).

Based on a review of prostate cancer treatment and screening trials, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) has stated that prostate-specific antigen (PSA)–based screening may not be necessary, saying that the potential benefits of the screening do not outweigh the potential harm of complications from evaluations and treatments.

Radium-223, an alpha particle given intravenously, has been shown to improve overall survival in men with castrate-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC), with a 30% risk reduction of death (HR = 0.695, P = 0.00185).

The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved two new indications for the osteoporosis drug denosumab, as a treatment for bone loss in men receiving androgen deprivation therapy for nonmetastatic prostate cancer and in women receiving adjuvant aromatase inhibitor therapy for breast cancer.
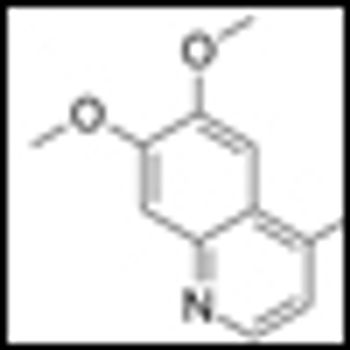
Cabozantinib (cabo), formerly known as XL184, has recently shown unprecedented activity against bone metastases in prostate cancer patients in a phase II trial.
Researchers have found that patients with early, localized prostate cancer benefit from short-term androgen-deprivation therapy (ADT) for 4 months prior to and during radiotherapy, and that the addition of ADT increases overall survival and decreases mortality.
Scientists at the Center for Translational Pathology and the department of urology at the University of Michigan Medical School have developed a new noninvasive urine test for prostate cancer that may be able to stratify patients by risk.

Hoppe et al present an excellent review of the physics relevant to an understanding of proton therapy-and of the available literature assessing the use of proton beams in the management of prostate cancer.

Fifteen years from now, graduate business school students seeking a PhD in medical economics will write dissertations on the topic of proton therapy and its place in the health care reform efforts of the 2010s

This review discusses the rationale, history, and current status of proton therapy for prostate cancer-and controversies regarding it.

At the session on Management of Prostate Cancer in Older Adults: To Treat or not to Treat, Anthony D’Amico, William Dale, and Shabbir Alibhai all lent their clinical expertise in treating prostate cancer to outline the latest recommendations for screening and treating men for prostate cancer.
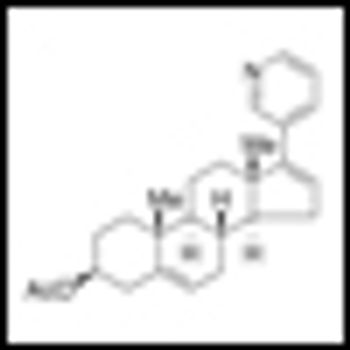
Abiraterone acetate has been shown to significantly acetate prolonged overall survival among patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) who previously received chemotherapy. The results of the Phase III study were published in the May 26, 2011 edition of the New England Journal of Medicine.

Drs. Ruch and Hussain provide an excellent overview of the emerging therapeutic agents and targets for advanced prostate cancer.

The article by Ruch and Hussain provides a comprehensive overview of the progress that has been made in translating basic science findings in prostate cancer biology to clinical trials.

This article will present a detailed review of the body of evidence regarding the PSA assay, with reflections on the resulting future of prostate cancer screening.

This review will discuss recently FDA-approved agents for advanced prostate cancer and those under investigation in phase III trials.

A study published in the journal Cancer on May 9 has now specifically examined the outcome of cancer survivorship of the gay, lesbian, and bisexual population. The study authors found that cancer outcomes differ based on sexual orientation.

Prostate cancer screening using prostate-specific antigen (PSA) testing has been a contentious subject.

The controversy surrounding PSA screening is one of the most heated in oncology. The potential benefits include prevention of prostate cancer morbidity and mortality, but the men potentially harmed through overdiagnosis and overtreatment outnumber those who benefit.
A large-scale, retrospective study published in the JNCI has now shown that men who take statins had lower incidence of total and high-grade prostate cancer compared with men who took antihypertensive medications.