
Matthew S. Davids, MD, MMSc, discussed his phase I/II study of duvalisib combined with venetoclax for patients with relapsed/refractory CLL and SLL at the ASH Annual Meeting & Exposition.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


Matthew S. Davids, MD, MMSc, discussed his phase I/II study of duvalisib combined with venetoclax for patients with relapsed/refractory CLL and SLL at the ASH Annual Meeting & Exposition.
The combination of ibrutinib and rituximab demonstrated superior progression-free survival in older patients with previously untreated chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
The triplet regimen consisting of acalabrutinib, venetoclax, and obinutuzumab appeared highly active as frontline therapy for patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
Lisocabtagene maraleucel induced high response rates in patients with aggressive relapsed/refractory large B-cell lymphoma.
Treatment with lenalidomide and rituximab improved progression-free survival, compared with placebo in patients ≥70 years old with indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
The combination use of polatuzumab-vedotin, obinutuzumab, and lenalidomide showed high complete response rates in patients with relapsed/refractory follicular lymphoma.
Acalabrutinib alone and in combination with obinutuzumab significantly improved progression-free survival, compared with obinutuzumab plus chlorambucil in treatment-naïve patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia
First-line treatment with ibrutinib plus venetoclax provided high rates of undetectable minimal residual disease in peripheral blood and bone marrow of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
Mosunetuzumab generated durable responses in patients with highly refractory non-Hodgkin lymphomas.
The CAR T-cell therapy axicabtagene ciloleucel induced a median overall survival of 25.8 months for patients with refractory large B-cell lymphoma.

The FDA granted a breakthrough therapy designation to abatacept for the prevention of moderate to severe acute graft-versus-host disease in hematopoietic stem cell transplants from unrelated donors.
Additional positive interim safety and efficacy data were reported for annamycin in the treatment of patients with relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia.

As part of Project Orbis, The FDA has approved acalabrutinib for the treatment of adult patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia or small lymphocytic lymphoma.
A new study in the Journal of Clinical Oncology finds that a subset of pediatric ALL relapses may be triggered by the very chemotherapy which helped patients beat the cancer the first time.

The National Comprehensive Cancer Network recently issued new guidelines on best practices in evaluating patients for hematopoietic cell transplantation, as well as how to manage complications associated with the procedure.
Treatment with gilteritinib improved survival and increased remission rates, compared with salvage chemotherapy, among patients with relapsed or refractory FLT3-mutated acute myeloid leukemia.
Treatment with SY-1425 in combination with azacitidine induced a 62% complete response rate with incomplete blood count recovery rate among unfit patients with RARA-positive AML.

Jennifer Crombie, MD, discusses classification of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) into distinct subtypes and treatment decisions based on molecular classifications.
Researchers explore the predictive capability of EVI1 expression.
Researchers report on the BRIGHT AML 1019 Phase III trial.
MYC-rearrangement within 2 years after diagnosis may affect the prognosis of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.
A new study looks into whether disease stage at diagnosis affects the occurrence and location of a second primary malignancy in DLBCL.
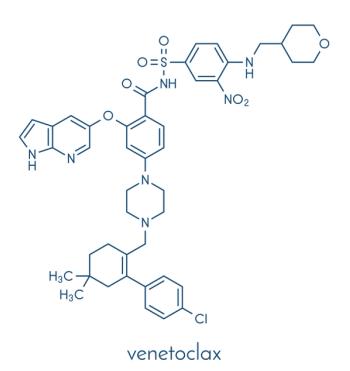
With FDA-approved indications for both chronic lymphocytic leukemia and acute myeloid leukemia, and continued investigation within multiple disease states, venetoclax has become an exciting oral targeted therapy among oncologists.
In this study, FLT3-IRAK1/4 inhibitor (NCGC1481) removed adaptively resistant FLT3-mutant AML cells.
Prognostic signature associated with AML relapse risk potential harbors gene subsets that apply to only certain patient subgroups.