
This article summarizes the existing literature on use of radiotherapy for node-positive prostate cancer, as well as the associated outcomes.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


This article summarizes the existing literature on use of radiotherapy for node-positive prostate cancer, as well as the associated outcomes.

We are in urgent need of a randomized trial comparing radiation plus ADT vs ADT alone for men with node-positive prostate cancer.

Despite the lack of level 1 evidence, retrospective studies support the need for appropriate local treatment, even in the context of node-positive disease.

A targeted magnetic resonance/ultrasound fusion–guided biopsy technique produced better results than a standard biopsy for detecting high-risk prostate cancer.

Prostate cancer patients who smoke may be more susceptible to complications from treatment, and have increased risk of side effects and disease recurrence.

Group exercise programs can improve the physical and mental well-being of prostate cancer patients, as well as providing emotional and social support.

As a variety of new hormonal agents are increasing survival times for men with metastatic disease, it is becoming increasingly important to consider cardiovascular, renal, and other potentially more serious risks associated with long-term ADT, especially in an aging population.

The problem with large sets of data is the risk of the “GIGO” principle-viz. garbage in, garbage out-and it requires a very careful and thoughtful investigator to rule out the many errors of large-scale data capture.
This article reviews recent evidence suggesting an increased risk of pneumonia, cardiovascular disease, and acute kidney injury in men treated with ADT and consider whether the incidence of such events differs with the treatment modality.

A small study found that testosterone may suppress the growth of some advanced prostate cancers and could reverse resistance to testosterone-blocking agents.
Older men who received radiotherapy in addition to ADT had fewer deaths from their locally advanced prostate cancer compared with those treated with ADT alone.

Extending the duration of androgen suppression in men with intermediate-risk prostate cancer prior to radiotherapy led to more adverse events and did not improve outcomes.

The purpose of this article is to present an updated set of American College of Radiology consensus guidelines formed from an expert panel on the appropriate use of radiation therapy in postprostatectomy prostate cancer.
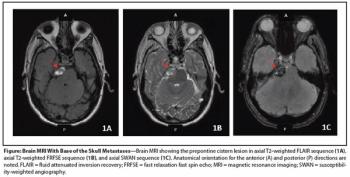
A 63-year-old man with no family history of prostate cancer has prostate biopsy that revealed 9 out of 12 cores involved with prostatic adenocarcinoma, mostly Gleason score 5+4=9.

Molecular imaging in prostate cancer can play the additional critical role of an early biomarker for response to therapy, similar to how 18F-FDG is used in other malignancies.
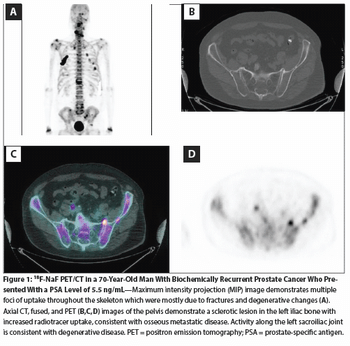
We briefly review these two imaging technologies and provide potential utilization strategies based on available data.
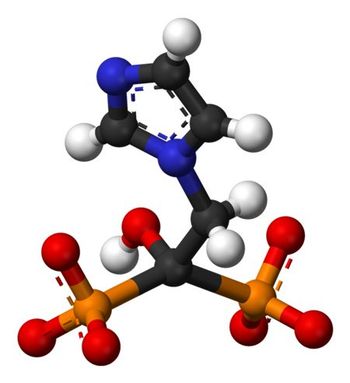
Despite recommendations calling for their use, prescriptions for bisphosphonates among older men with prostate cancer undergoing ADT are still low.

The use of a prostate cancer antigen 3 urine test could help men avoid undergoing unnecessary repeat biopsies, and predict which will be positive for cancer.

Clinical trial results to date show that men with visceral CRPC metastases do not benefit from ipilimumab, while their counterparts with bone- or node-only metastases do. This suggests that visceral metastases should be a stratification factor for future immunotherapy clinical trials.

While evidence points to benefit from highly active hormonal agents in prostate cancer with visceral involvement, the usefulness of immunotherapy is much less clear.
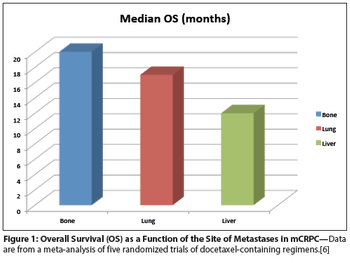
Although the mechanism(s) underlying the relatively poor prognosis of prostate cancer patients with visceral disease have yet to be fully elucidated, these new findings suggest that the microenvironment of bone lesions may be immunologically distinct from those at other sites.

One should not advise a patient with low- or very-low-risk prostate cancer to undergo a focal ablation. The kindest and gentlest approach is to first do no harm.

Investigators and physicians caring for the spectrum of prostate cancer should have a targeted treatment option available for patients who would benefit by it.

A study found that prostate cancer patients with a history of heart problems are at increased risk of cardiac death following androgen-deprivation therapy.

Ultimately, while further follow-up will be enlightening, we believe that there is sufficient evidence now from the primary analysis of CHAARTED to justify the combination of docetaxel and androgen deprivation therapy in all men with metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer.